
- Trump signed an Executive Order imposing a 25% tariff on Canada and Mexico, and a 10% tariff on China. The tariff to Mexico was then delayed by one month.
- Investors continued to digest the impact of DeepSeek on the AI story.
- The Indian government published its 2025 budget.
- Political developments in Argentina.
- Brazil’s President Lula reaffirmed commitment to primary deficit reduction.
- Colombia’s President Petro announced a new tax reform aimed at funding infrastructure projects.
- Panama’s President Mulino pledged free passage for US warships through the Panama Canal, while reiterating Panama will not relinquish control.
- Kuwait expected to approve new law allowing first debt issuance in eight years.
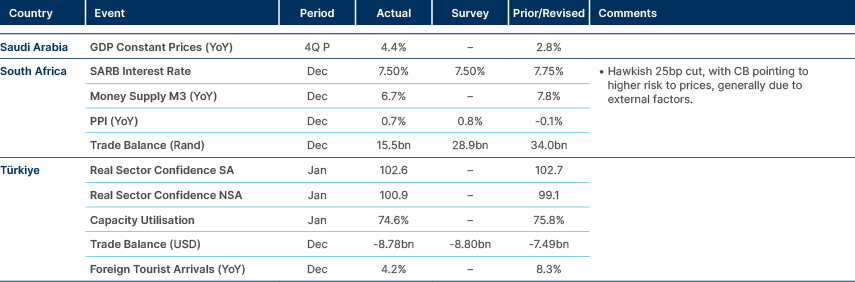
- Donald Trump cuts foreign aid to South Africa but impact relatively immaterial.
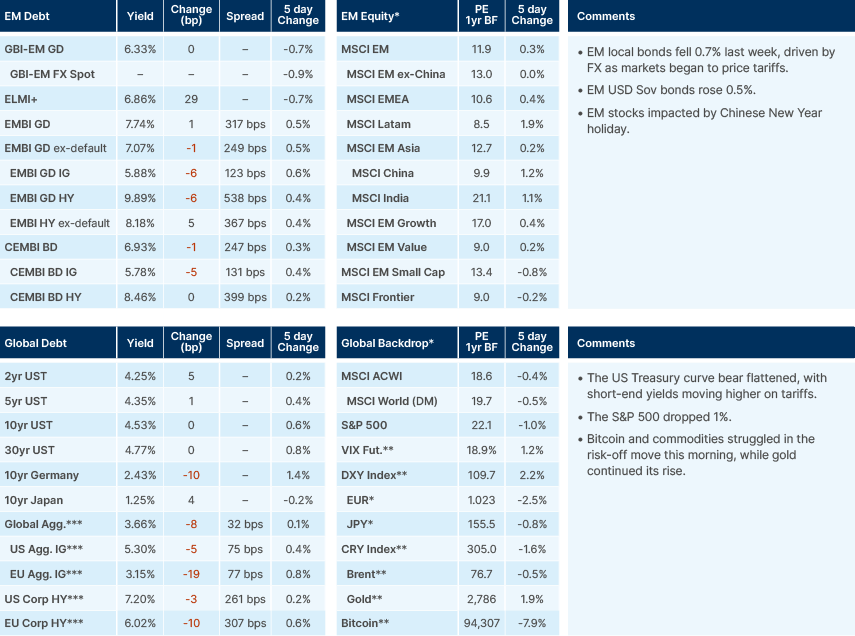
Last week performance and comments
Global Macro
Tariffs
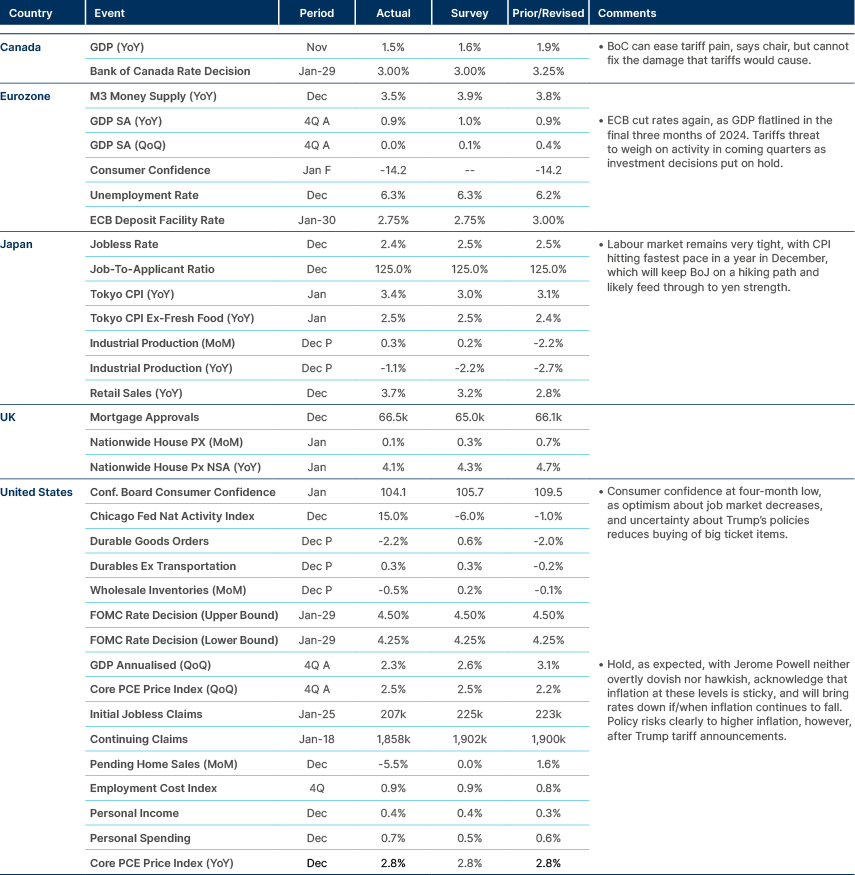
On Saturday, US President Donald Trump signed an Executive Order imposing comprehensive tariffs: 25% on imports from Mexico and Canada, and 10% on imports from China, effective 4 February. An exception applies to Canadian energy exports, which will face a 10% tariff. Trump invoked the International Emergency Economic Powers Act, citing national security threats from illegal immigration and fentanyl trafficking through the Mexican and Canadian borders. The Executive Order may face court challenges.
In response, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau announced a 25% counter-tariff on USD 107bn of US substitutable goods. Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum pledged retaliatory measures, both tariff and non-tariff. China plans to challenge the tariffs at the World Trade Organization. Later on Monday, Donald Trump and Claudia Sheinbaum came to an agreement to postpone the tariff by a month, with Sheinbaum sending 10.000 Mexican National Guard troops to join the effort at the border to stop drugs and migrants illegally entering the US. Canada have not yet had the same exit opportunity.
If tariffs are eventually fully implemented, US economic growth is likely to decline, and inflation will increase. Mexico and Canada would feel a stronger impact on their economies given the relative size of the US market. In terms of market prices, we would expect interest rate cuts from the US Federal Reserve (Fed) to be priced out, but the yield curve should flatten considering the impact on gross domestic product (GDP) growth. The Dollar is likely to strengthen in the short term, and equity prices should decline. It feels like the market has anticipated the impact of broader tariffs in emerging market (EM) assets, particularly EM currencies such as the Mexican Peso, but not yet in US stock markets.
We remain of the view that a negotiated reduction in tariffs, possibly settling around 10% for revenue purposes, seems probable in the coming weeks. The Executive Orders suggest that reductions in migration and drug flows could serve as an ‘off-ramp’ for lowering tariffs, though specific benchmarks remain undefined. It seems Trump is prepared to accept inflationary risks to fulfil his campaign promises, using tariffs not only as a border control tool but also to support US fiscal objectives. On the other hand, if implemented and maintained as announced, tariffs are likely to trigger a backlash from American businesses. Within a few months, it would also be clear to the US population that tariffs did impact their lives via higher costs for energy, food, durable and non-durable goods, and maybe jobs.
Commodities
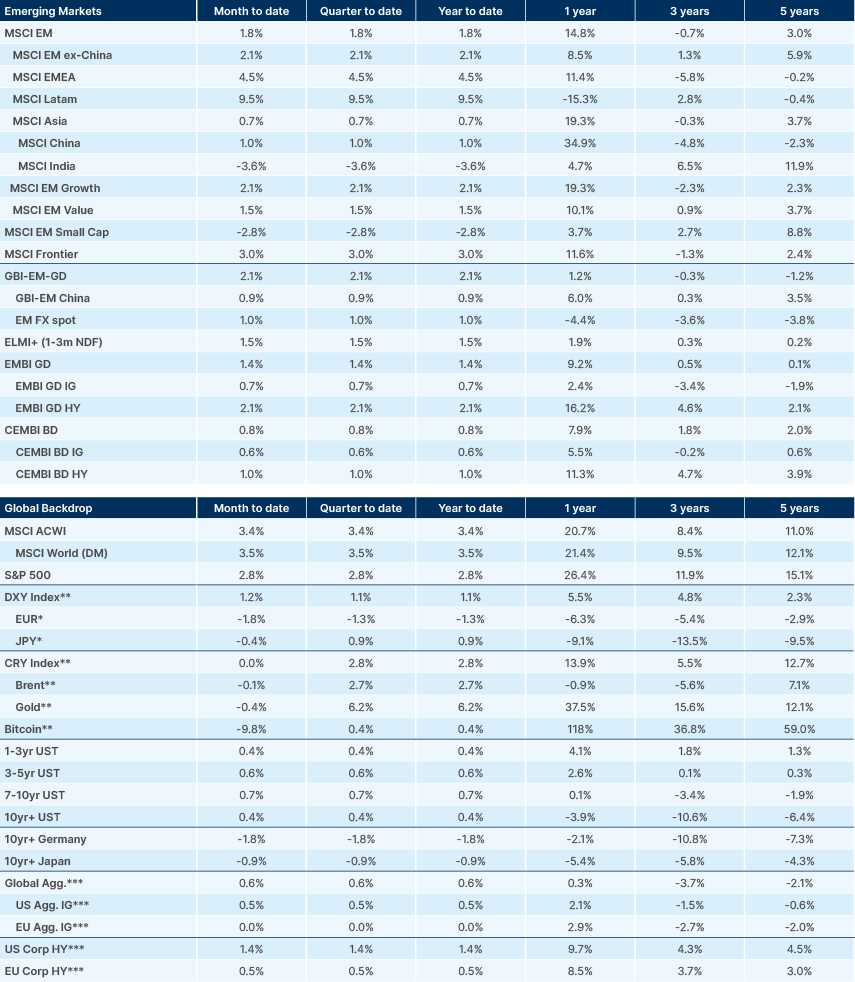
Gold surged to a record high last Thursday, rising 7% in January despite increasing interest rates. Traditionally, gold thrives in low-rate environments due to its non-yielding nature. This rally reflects strong safe haven demand amid concerns over US economic policies. Additionally, EM central banks continue to accumulate gold reserves, reinforcing its bullish momentum.
Emerging Markets
Asia
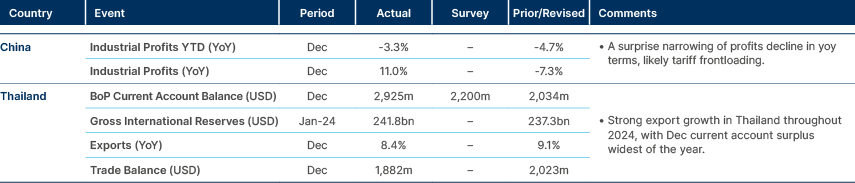
Fiscal austerity in India and Malaysia. Sharp slowdown in Indonesia’s CPI
India: In a budget released on Saturday, the government tabled a cut in the FY26 deficit to 4.4% of GDP. This budget aims to stimulate economic activity, enhance infrastructure, and support various demographics, particularly the middle class, women entrepreneurs, and rural communities. The most important measure was to significantly increase the threshold for low income individuals paying taxes from INR 700,000 to INR 1.28m. This will be helpful in supporting consumption.
The budget was good news for the macroeconomic foundation, even if not well received by the market. Indian stocks related to infrastructure underperformed post news. The currency sold off due to tariff uncertainties and well as the expectation that the central bank may have more room to cut policy rates on the back of a better balanced budget.
Indonesia: Consumer price index (CPI) inflation slowed to 0.8% yoy in January from 1.6% yoy in December 2024. The sharp slowdown was mainly on the back of utility prices, reflecting the electricity tariff cut. President Prabowo Subianto said social programmes will not be affected by the order for ministries to cut total spending by IDR 306.7tn (USD 18.9bn) in 2025. Prabowo’s approval reached 80.9% after his first 100 days in office. This compares with 65.1% for his predecessor Joko Widodo. The free meal programme and scaling down the VAT rate cut supported Prabowo's rating.
Malaysia: The federal government’s fiscal deficit fell 18% yoy to MYR 74.9bn in 2024. This was substantially lower than the government’s revised estimate of MYR 84.3bn deficit for the year. This probably brings the fiscal deficit close to 3.8% of GDP, 50 basis points (bps) below the government target at 4.3%.
Philippines: GDP rose by 5.2% yoy in Q4, below expectations. The growth miss was driven by poorer performance of agriculture and fishing sectors, hit by six typhoons.
Latin America
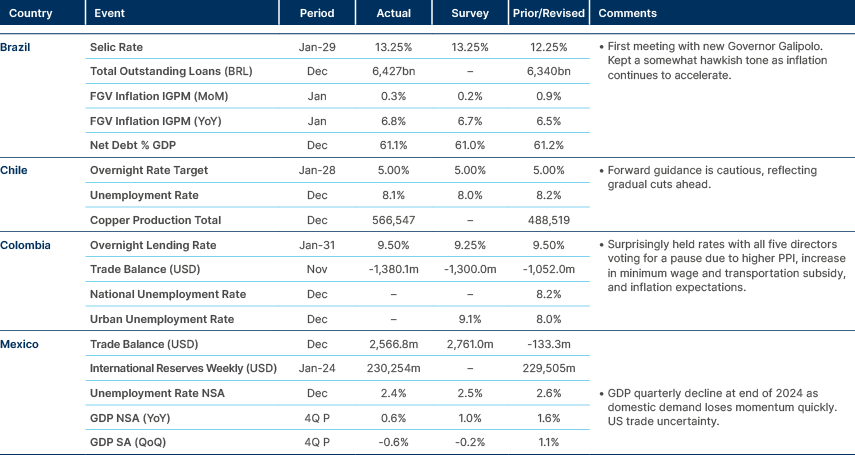
Weaker momentum on Mexican economy. Colombia policy unchanged.
Argentina: The Central Bank of Argentina reduced interest rates by 300bps to 29% overnight. This weekend, the reduction in the ARS crawling peg from 2% to 1% will come into effect.
Senator Alfredo de Angeli, of the Republican Proposal Party (PRO) stated that a partial alliance with the ruling Freedom Advances (LLA), for the mid-term elections could be determined on a district-by-district basis. Both parties share similar ideologies and seek significant reforms. The primary objective is to consolidate the liberal vote and prevent left-wing Peronists from gaining ground. PRO prefers district-level negotiations to maintain more governmental influence, for example in Buenos Aires city district. Milei, on the other hand, has said recently that any alliance would have to be nationwide, or it would not happen at all.
Economy Minister Luis Caputo criticised analysts for consistently misjudging the preconditions of the deal with the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Key rumours included:
- A shift from the current crawling peg to exchange rate intervention bands.
- A two-step IMF programme, starting with a looser plan in 2025, followed by an Extended Fund Facility (EFF) to accelerate currency flotation and remove foreign exchange (FX) controls.
- Conflicting reports regarding new IMF disbursements, with estimates ranging from USD 5bn to USD 10bn.
Brazil: President Lula reaffirmed his commitment to fiscal responsibility, emphasising the reduction of the primary deficit to 0.1% of GDP in 2024. Although no immediate fiscal measures are planned, the government will reassess the situation as needed. Lula assured there would be no drastic actions concerning food prices, anticipating that a record harvest will help ease inflation. While Petrobras may delay gasoline price increases, diesel prices are expected to rise.
Lula refrained from directly criticising the central bank’s decision to raise the Selic rate to 13.25%. In, response to the potential imposition of US tariffs under President Trump, Lula warned that Brazil would adopt reciprocal measures. This stance contrasts with Finance Minister Haddad, who indicated the possibility of new fiscal measures following the 2025 budget discussions.
The central government recorded a BRL 24bn surplus in December, reducing the primary deficit to 0.1% of GDP in 2024. Federal revenue increased by 14.4% to BRL 2.6trn, marking a record high. However, fiscal expert Marcos Mendes noted that adjustments – including unrecorded expenses, temporary measures, and Petrobras-related settlements – bring the true deficit to 2.1% of GDP. Without these one-off measures, the recurring deficit would stand at 1.7% of GDP.
In December, formal job creation decreased by 535,000, significantly exceeding the expected decline of 403,000 due to seasonal weakness. All five sectors reported job losses during this period. Nevertheless, formal job creation rose by 17% to 1.7m in 2024.
Chile: The Senate approved a pension reform bill with 40 votes in favour and seven against. The bill now proceeds to the lower house, where swift ratification is anticipated this week.
Colombia: President Gustavo Petro announced a new tax reform aimed at funding infrastructure projects, addressing criticism over budget postponements. The Finance Ministry postponed COP 12trn in spending from the 2025 budget to COP 511trn.
Petro warned that if the reform is rejected, the postponed expenditures would result in budget cuts. The government is considering tax increases on gambling, online gaming, and other sectors. A previous tax bill was shelved by Congress, but linking new taxes to critical infrastructure projects may pressure the opposition into support.
Ecuador: Recent polls indicate that market-friendly President Daniel Noboa has a voting intention of 41.4%, compared to 27.6% for left-wing candidate Luisa Gonzalez in second place. This development led to a rise in Ecuadorian bonds above distressed levels for the first time in two years, with the spread over US Treasuries falling below 10%.
The survey suggests Noboa's chances of winning outright in the first round are increasing. To achieve this, a candidate must secure 50% plus one of the valid votes or at least 40% with a 10-point lead over the runner-up.
Panama: Panama has pledged to provide free passage for US warships through the Panama Canal and announced its withdrawal from China’s signature lending programme, following a meeting between US Senator Marco Rubio and President José Raúl Mulino. President Mulino reaffirmed Panama's sovereignty, stating the country will not relinquish control of the Canal.
Central and Eastern Europe
Stronger GDP in Hungary
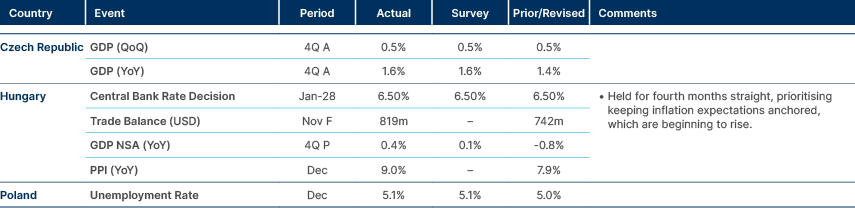
Hungary: The opposition Tisza Party currently leads the ruling Fidesz Party by five percentage points in polls. The Tisza Party has garnered 42% support among decided voters who are certain to vote, compared with 37% for Fidesz. It is noteworthy that this poll was conducted by the left-leaning Publicus pollster. While most of the population desires a change in government, there is a prevailing sentiment that such a change is unlikely to occur in the 2026 elections, and the incumbent Viktor Orbán is likely to retain power.
Central Asia, Middle East, and Africa
Inflation surprised to the upside in Türkiye
Angola: Petrobras signalled interest in Angola’s oil potential amid expansion plans. Local fields have technical and geological similarities with Brazil's Campos, Santos, and Pelotas basins.
Egypt: Fitch Solutions projects a 2.5% increase in gas production in 2025, followed by an additional 1.0% increase in 2026, as drilling operations at Zohr resume.
Kuwait: Kuwait is expected to approve a new law allowing for the country’s first debt issuance in eight years. The new law could enable USD 65bn of issuance over the next 50 years. Kuwait’s debt/GDP ratio is currently just 7%, the IMF sees this figure rising to 25% by 2029.
Lebanon: The Saudi Arabian Foreign Minister, Prince Faisal bin Farhan, voiced optimism about Lebanon’s future as reforms pledged by new President Joseph Aoun would boost confidence in Lebanon among international partners. The Prince visited Lebanon last week, and also reiterated support for the US-brokered ceasefire agreement that ended the war between Israel and Hezbollah. This was the first diplomatic trip to Beirut by a Saudi Foreign Minister for 15 years.
Saudi Arabia: Fitch affirmed Saudi Arabia’s credit rating at A+ with a Stable outlook.
South Africa: Donald Trump announced the US will be cutting off all future aid to South Africa due to land-seizure policies. However, South Africa’s funding from the US is relatively limited, receiving USD 280m in obligations and USD 380m in disbursements in 2024.
Türkiye: CPI inflation surprised to the upside on Monday morning (42.1% yoy vs 41.1% consensus; 5.0% mom vs 4.3% consensus). This was driven by services, particularly health, education and rent, as core CPI inflation also surprised to the upside at 42.7% yoy.
Developed Markets
ECB dovish tone. Fed waiting for policy impact.
Benchmark Performance
Source and notations for all tables in this document:
Source: Bloomberg, JP Morgan, Barclays, Merrill Lynch, Chicago Board Options Exchange, Thomson Reuters, MSCI. Latest data available on publication date.
* Price only. Does not include carry. ** Global Indices from Bloomberg. Price to Earnings: 12m blended-forward
Index Definitions:
VIX Index = Chicago Board Options Exchange SPX Volatility Index. DXY Index = The Dollar Index. CRY Index = Thomson Reuters/CoreCommodity CRM Commodity Index.
Figures for more than one year are annualised other than in the case of currencies, commodities and the VIX, DXY and CRY which are shown as percentage change.