
Solid forward looking PMI's across Asia and technical bear flattening of DM yield curves
Manufacturing PMIs were stronger than expected in Indonesia, India, Malaysia and Thailand (snippets). The front end of global DM curves widened significantly, leading to further “bear” flattening across global yield curves (Global backdrop). China’s regulators increase scrutiny over property developer’s debt payments and announced energy transition targets for the next 10 years. Brazil hiked rates by 150bps to 7.75% while Colombia hiked 50bps to 2.50%. Chile`s copper production dropped to its lowest level in 10 years. Dominican Republic opted not to hike taxes and Malaysia announced another sizeable fiscal deficit in 2022. Mexico`s Pemex said the government will settle its foreign debt and Pemex would not issue Eurobonds in the near future. Pakistan received USD 4.2bn assistance from Saudi Arabia and narrowed its differences with the IMF. South Korean export growth softened, but remained at elevated levels. In Turkey, President Erdogan dropped the demand to expel 10 ambassadors from the country, a sign his grip on power is declining.
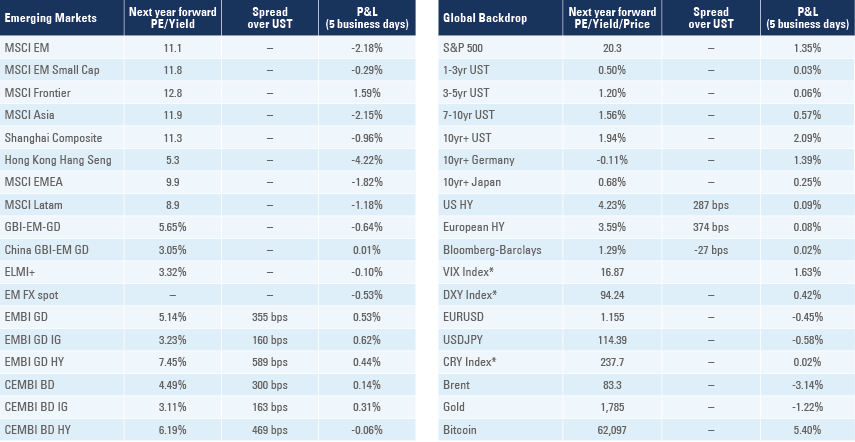
Emerging Markets
Brazil: The Brazilian Central Bank hiked the policy rate by 150bps to 7.75%, in line with consensus. CPI inflation rose 1.2% mom in the first 15 days of October to 10.3% yoy, above the 10.1% yoy (both prior and consensus). Most inflationary pressures came from supply shocks from energy and food prices due to the drought as well as higher transportation prices due to higher fuel prices. Fiscal data surprised to the upside, as tax collections rose to BRL 149bn in September from BRL 146bn in August, allowing the budget balance to move to a BRL 0.3bn primary surplus from a BRL 9.9bn deficit and the net debt/GDP ratio to decline to 58.5% from 59.3% over the same period. Despite the better fiscal results, Brazilian assets remained unanchored due to fiscal uncertainties as the government struggles to approve the 2022 budget. In labour market news, 312k new jobs were created in September from 372k in August.
China: The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE) held a joint meeting with major real estate developers. Authorities asked developers to “prepare" to meet payments on their offshore bonds and asked those developers that were due to miss payments to notify SAFE first, according to Caixin. Regulators stressed they would support developer’s “reasonable needs" for the rollover of foreign debt. Last week, Chinese authorities urged Evergrande founder Hui Kay Yan to use his personal fortune to support the company and Bloomberg reported he pledged his Hong Kong house worth HKD 300m (USD 38.6m) against a personal loan.
On the energy side, the NDRC announced they are exploring options to “cool down” coal prices by “prohibiting exorbitant profits”. Xi Jinping did not attend the 26th session of the United Nations Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP-26), but China unveiled ambitious and detailed energy transitions plans for the next 10 years as per Figure 1:
Figure 1: China’s near term energy transition goals

In economic news, the Caixin manufacturing PMI rose 0.6 to 50.6, contrasting with the NBS manufacturing PMI that dropped 0.4 to 49.2 in October as non-manufacturing PMI declined 0.8 to 52.4 over the same period. Industrial profits rose by 16.3% on a yoy basis in September from 10.1% yoy in August. China`s steel production declined 21.2% in September to 74 Mt, and increased 2.0% year-to-September at 806 Mt. The top-10 steel producing nations ex-China increased production by 15.1% yoy to 439 Mt year-to-September, highlighting China’s importance in the steel industry.
Chile: Total copper production dropped 15k to 451k tons in September, the lowest level for the period since 2011 and 5% lower than average of the past 10 years. The unemployment rate declined 0.1% to 8.4% in September. The yoy rate of retail sales dropped 5.2% to 19.9% in September while manufacturing production dropped 6.3% to 4.3% yoy over the same period.
Colombia: The central bank hiked its policy rate by 50bps to 2.5%, 25bps above consensus and signaled a faster pace of increase going forward. The urban unemployment rate dropped 1.2% to 13% in September while the national unemployment declined 0.2% to 12.1%. Industrial confidence rose 4.8 to 20.4 and retail confidence declined 3.2 to 40.3.
Dominican Republic: President Abinader announced the government will adjust the budget deficit via controlling expenditures instead of increasing taxation. The country is already undertaking one of the largest fiscal adjustments across Latin America, placing debt on downward path.
Pakistan: Saudi Arabia pledged to provide USD 4.2 billion in assistance to Pakistan, including a USD 3bn deposit by the Saudi Fund for Development in the State Bank of Pakistan and a USD 1.2bn facility to finance oil derivatives trade. Pakistan Finance Minister Shaukat Tarin said the country settled its differences with the IMF, an important step to reaching a programme.
Malaysia: The government announced a fiscal deficit of 6.0% on its 2022 budget and a 5.5% to 6.5% GDP growth target (from 3.0% to 4.0% in 2021). The limited fiscal consolidation alongside high vaccination rates and lower restrictions is likely to add pressure on Bank Negara Malaysia to increase policy rates in the future, in our view. In economic news, the Markit manufacturing PMI rose 4.1 to 52.2. The trade surplus was unchanged at MYR 26.1bn in September, MYR 3.5bn above consensus as exports expanded by 24.7% yoy (from 18.4% yoy) and imports rose 26.5% yoy (from 12.5% yoy) over the same period
Mexico: Octavio Romero, the CEO of state-owned oil company Pemex, told congress the government will pay Pemex coupons and amortisations and Pemex would no longer issue foreign bonds. The yoy rate of real GDP growth declined to 4.6% in Q3 2021, 1.4% below consensus, but the unemployment rate dropped 0.1% to 4.2% in September and the trade deficit narrowed to USD 2.4bn in September from USD 3.9bn in August.
South Korea: The trade surplus narrowed to USD 1.7bn in October (USD 2.1bn consensus) from USD 4.2bn in September as the yoy rate of export growth slowed to 24.0% in October, 4.5% below consensus while imports accelerated to 37.8% yoy (43.0% consensus) from 31.0% prior. The Markit manufacturing PMI softened 2.2 to 50.2 in October. GDP growth slowed to 0.3% q/q in the three months to September, down 0.5% from the previous quarter, taking the yoy rate to 4.0% from 6.0% yoy over the same period. Private consumption, services as well as fixed investments all slowed down over the last quarter.
Turkey: President Erdogan dropped his demand for 10 ambassadors to be expelled, deescalating a diplomatic row that, alongside with the CBRT cut, contributed to a 6% plunge in the TRY the previous week. Erdogan’s unusual U-turn suggests his grip on power is softening as political checks and balances are at work. In economic news, the trade deficit moderated to USD 2.6bn in September from USD 4.3bn in the previous month. A total of 17.5m tourists visited Turkey from January to September, 26.5% below the average of the last 15 years of 23.9m. In other news, the Markit manufacturing PMI declined 1.3 to 51.2 in October.
Snippets
Czech Republic: The yoy rate of real GDP growth slowed to 2.8% in Q3 2021 from 8.1% yoy in the previous quarter, 0.4% below consensus. Consumer confidence declined 2.0 to -8.5 in October while business confidence declined 0.7 to 6.7 over the same period.
Egypt: The Central Bank of Egypt kept its deposit and lending policy rates unchanged at 8.25% and 9.25% respectively, in line with consensus.
Hungary: The unemployment rate was unchanged at 4.0% in September while economic sentiment rose 3.0 to +2.5 in October and the yoy rate of average gross wages increased 1.0% to 8.9%
Kazakhstan: The central bank hiked its policy rate by 25bps to 9.75%, surprising consensus (3 out of 4 analysts expected no change).
India: The manufacturing PMI rose to 55.9 in October from 53.7 in September, driven by strong momentum in new orders, higher stock purchases and production while employment conditions remained weak.
Indonesia: The manufacturing PMI surged to 57.2 in October from 52.2 in September. The yoy rate of CPI inflation rose 0.1% to 1.7% while core inflation was unchanged at 1.3%.
Moldova: Gazprom reached a deal to extend gas supplies last week. The new contract will feature higher prices according to a formula proposed by the Moldovan government. Moldova also agreed to pay USD 700m of debts from previous gas supplies. The European Union pledged EUR 60m assistance to Moldova amid an energy crunch.
Nigeria: The current account deficit narrowed to USD 0.4bn in Q2 2021 from USD 2.1bn in Q1 2021. Nigeria’s external accounts should swing to a surplus should oil prices remain above USD 80 per barrel if oil production is to increase in line with OPEC allowance. Nigeria`s oil production declined to 1.6m barrels per day in May 2021 from an average of 2.0m between 2015 and 2020 and 2.4m from 2010 to 2015, according to data from EIA.2
Philippines: The overall balance of payment moved to a USD 0.4bn deficit in September from a 1.0bn surplus in August.
Poland: The yoy rate of CPI inflation rose 0.9% to 6.8%, 0.4% above consensus while the unemployment rate declined 0.2% to 5.6% in September.
Russia: The Markit manufacturing PMI rose 1.8 to 49.8 (1.1 above consensus). The yoy rate of industrial production rose 2.2% to 6.8% in September while retail sales dropped 0.7% to 2.2% yoy and the unemployment rate declined 0.1% to 4.3% over the same period. The weekly yoy rate of CPI inflation rose 0.3% to 6.3% on the 25 October.
Taiwan: The Markit manufacturing PMI rose 0.5 to 55.2 in October. The yoy rate of IP declined to 12.2% in September from 13.4% in August, 0.4% above consensus as GDP growth slowed to 3.8% annualized over Q3 2021 from 7.4% in Q2 2021, 0.5% lower than consensus.
Thailand: The Markit manufacturing PMI rose another 2.0 points to 50.9 in October. The current account deficit narrowed to USD 1.4bn in September from USD 2.5bn in August as exports rose by a 17.1% yoy rate in September from 8.9% yoy in August, significantly higher than consensus while the yoy rate of import growth declined to 20.4% from 39.6% yoy over the same period, below consensus.
Global backdrop
Rates: The front end of yield curves spiked last week after the Bank of Canada unexpectedly announced a taper of its government bond purchases and hinted at policy rate increases in 1H 2022. The Reserve Bank of Australia did not buy bonds after the April 2024 benchmark 0.1% yield target was breached, leading 2yr bonds to spike to 0.78% last week from 0.12% in the previous week. The front ends of global yield curves have been increasing in recent months as it has become clear that inflation is not transitory. The yield on 2yr US Treasuries widened to 0.50% last week from 0.22% in mid-September.
The overnight interest rate swaps now price the Bank of England’s first hike in November 2021, the Reserve Bank of Australia to hike in March 2022 and the Federal Reserve’s first hike by June 2022. Last week the European Central Bank (ECB) leaned against the aggressive move in short term rates as the 1y1y overnight interest rate swap moved from -0.50% in August to -0.08% on 29 October, pricing the first policy rate hike in Q4-2022 to Q1-2023 (from Q2 to Q3-2026 in August).
DM central banks are likely to hike policy rates reacting to higher inflation, but the magnitude of the hikes priced in the short term are starting to get excessive. The bear flattening of global yield curves was also exacerbated by technical factors, such as levered hedge funds stopping their losses, opening an opportunity for investors positioning for steeper curves.
Whereas flatter curves favour super-long duration assets such as US technology and unprofitable new businesses with super-long duration pay-out profiles, steeper curves tend to favour traditional companies with strong cash flow profiles (for example, commodity producers) trading at attractive valuations.
Coronavirus: Israel will allow people vaccinated with the Sputnik V vaccine entry to the country, according to the Jerusalem Post. Israel only allows people vaccinated with vaccines approved by the World Health Organisation (WHO), the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or European Medicines Agency (EMA), which have not yet approved the Sputnik V vaccine.
United States (US): The Biden administration unveiled a detailed outline for a USD 1.85trn build back better programme with no increase in public deficit. The smaller programme has a higher chance of Congress approval, albeit some of the tax elements may be adjusted. The proposal includes:
- USD 555bn in climate-related spending
- USD 600bn in child care and universal pre-school
- USD 150bn for affordable housing
- USD 150bn for elderly care and USD 130bn for healthcare credits
- USD 100bn for immigration reform
- USD 165bn across other spending items.
The key measures to raise revenues are:
- USD 480bn via 5% tax rise on individual incomes > USD 10m and further 3% > USD 25m and closing Medicare tax loopholes
- USD 450bn from 15% minimum tax on large corporations and 1% surcharge on equity buyback
- USD 400bn from IRS investments to reduce tax avoidance
- USD 350bn from 15% global minimum tax and other international tax measures
- USD 145bn from repealing the prescription drugs rebate rule implemented by Donald Trump
Economic data was overall better than expected as the Citibank Surprise index rose to-16.1 from -32.5 in the previous week. Initial jobless claims declined to 281k in the 23 October week from 291k in the previous week as continuing claims dropped to 2.22m in the 16 October week from 2.48m in the previous one. The University of Michigan 1yr inflation expectation was unchanged at 4.8% while the 5-10yrs oscillated 0.1% higher to 2.9%. The Conference Board consumer confidence rose 4 points to 113.8 and the MNI Chicago PMI rose 3.7 points to 68.4. Durable goods orders declined 0.4% in September after rising 1.3% in August. GDP growth slowed to 2.0% annualised in Q3 2021 from 6.7% in the previous quarter as the GDP price index moderated to a yoy rate of 5.7% from 6.1% yoy and the employment cost index rose 1.3% from 0.7% over the same period.
Eurozone: CPI inflation surprised to the upside as the yoy rate of CPI inflation rose 0.4% to 4.5% in Germany and 1.5% to 5.5% yoy in Spain driving the overall Eurozone CPI 0.7% higher to 4.1% yoy, driven by a large spike in energy prices as the core CPI inflation rose only 0.2% to 2.1% yoy. The French yoy rate of PPI inflation rose 1.6% to 11.6% in September while Italian PPI rose 1.8% to 15.6% yoy over the same period. The German IFO business climate survey declined 1.2 to 97.7 while IFO expectations was down 2.0 to 95.4 and current assessment was 0.3 lower to 100.1.
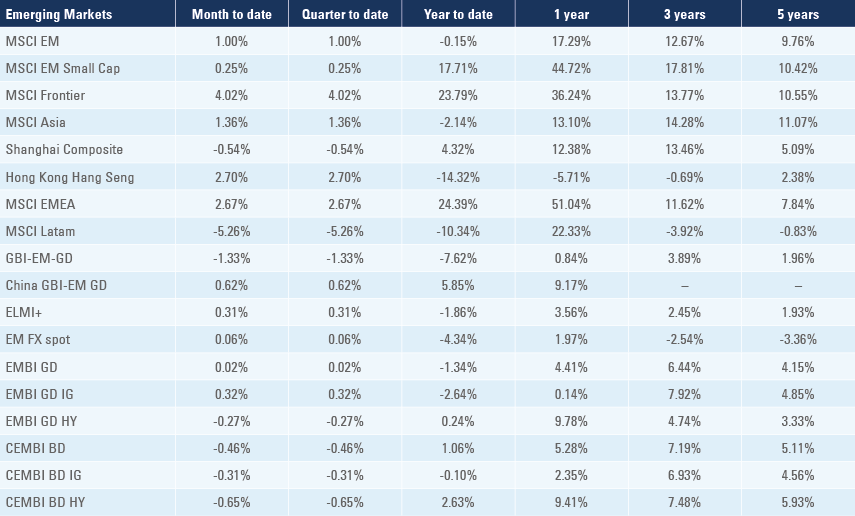
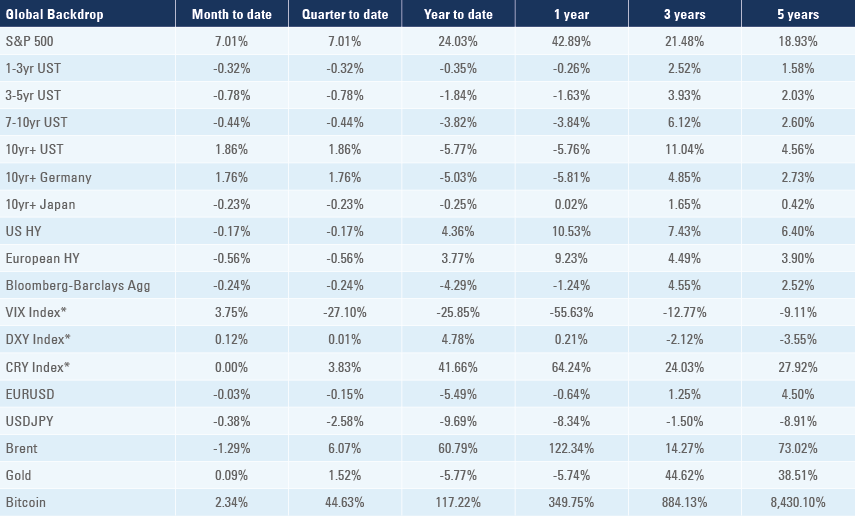
*VIX Index = Chicago Board Options Exchange SPX Volatility Index. *DXY Index = The Dollar Index. *CRY Index = Thomson Reuters / CoreCommodity CRM Commodity Index.
Source: Bloomberg, JP Morgan, Barclays, Merrill Lynch, Chicago Board Options Exchange, Thomson Reuters, MSCI, total returns.
Figures for more than one year are annualised other than in the case of currencies, commodities and the VIX, DXY and CRY which are shown as percentage change.
1. Steel scrap, copper, aluminium, lead, zinc, waste paper, plastic, rubber and glass
2. US Energy Information Administration