
The flash PMIs declined more than expected in Europe and the United States, with most forward-looking indicators below 50.0 levels. Russia agreed a deal to safeguard exports of grain from Ukraine and restarted gas flows from Nord Stream 1 pipeline but bombarded the port of Odesa next day. Argentina announced new measures to rein in currency depreciation in the parallel market. Brazil tax collections surprised to the upside again as debt/GDP stabilised earlier than expected. Chile unveiled its tax reform as Boric distances himself from the new constitution. China property staged a recovery this morning after reported measures to support the housing markets. Colombia’s economic activity still red hot. Ecuador bond prices recovered after President Lasso reached a deal with indigenous communities lowering social risks. Indonesia’s president travelled to China to meet his counterpart. US and Canada announced retaliatory measures against Mexico’s energy policies. Pakistan currency depreciated the most in a week since 1998. South Africa hiked policy rate by 75bps to 5.75%. Uruguay seeks a free trade agreement with China and Zambia said it reached a deal with official creditors, paving the way for an IMF agreement.
DM Flash PMIs
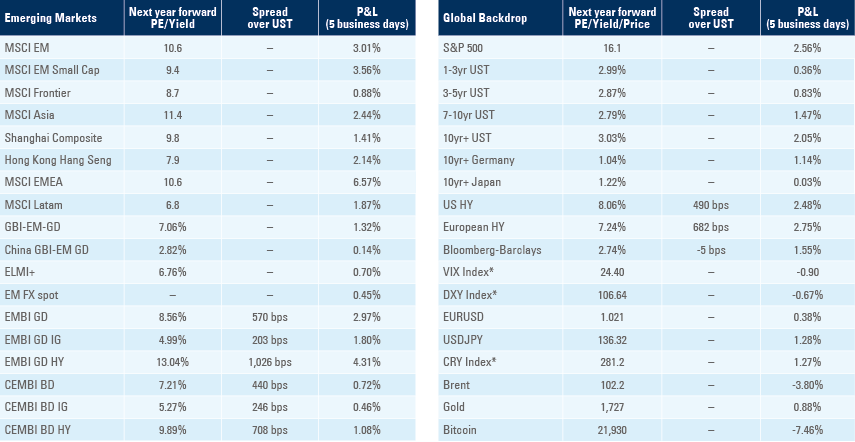
The flash PMIs for July declined across the board in DM, with Manufacturing PMI declining below 50 in France and Germany and staying marginally above 50 in the United States and United Kingdom as per figure 1. The key sub-components, new orders and current output, declined below 50 across the four countries, suggesting these economies are already experiencing the first signs of a mild recession.
Figure 1: Flash Manufacturing PMIs by country
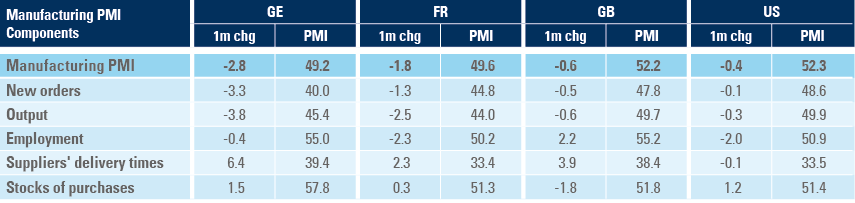
Service PMIs remained above 50 in France and the UK but declined below 50 in Germany and the US. The US service PMI dropped 5.7 points to 47.0 as per Figure 2 with most sub-components dropping more than expected.
Figure 2: US Flash Services PMI
Geopolitics
Russia resumed the flow of gas via the Nord Stream 1 pipeline on the 21 July after 10 days of interruption for maintenance. The resumption of gas flows reduced the risk of an energy crisis in the short term in Europe but allows Russia to retain leverage over Europe until at least the end of the 2022-23 winter season. Russian President Vladimir Putin said Saudi Crown Prince Salman emphasised continued cooperation within OPEC+ in a phone call.
An agreement allowing free transit of grain produce from Odesa and other two ports was signed in Istanbul. The deal was mediated by Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan. Turkey imported close to 25% of key grains and seeds from Russia1. Despite the agreement, Ukraine reported Russian forces bombarded the port of Odesa hitting grain silos and loading facilities one day after the agreement was signed, a reminder that Russia retains the ability to shutdown any trade flows that do not suit its strategic objectives. Russia claims it did not hit the port’s storage facilities, but “targeted military infrastructure”. Ukraine is requesting shippers to form an export caravan to start freeing the grain silos for the current production. Ukraine will also need to remove all sea mines around the port, a process that should take up to two weeks and leave the port vulnerable. BNP estimated around 60% of the current harvest is lost, stolen, or stuck in silos.
Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov said the grain shortages are due to the private sector exaggerating the implementation of sanctions imposed by the West. Lavrov said earlier that peace talks with Kyiv made no sense “in current situation”.
Ukraine launched a consent solicitation aiming to extend Eurobond payments that most likely will be successful as the Paris Club said its creditors agreed to halt Ukraine’s loan payment obligations until the end of 2023. While this should prevent a default over the next two years, the macroeconomic situation has deteriorated and the ability to pay severely impacted by the economic chaos and infrastructure destruction caused by the war, which is very likely to lead to another round of debt restructuring in the coming years. Despite significant aid from US, EU and multilateral institutions, Ukraine’s foreign exchange (FX) reserves declined from USD 29.4bn in December 2021 to USD 19.9bn in June and the UAH depreciated by 25% to 36.6 in July. The ratings agency Fitch downgraded Ukraine credit rating to `C`.
In contrast with the challenging monetary and fiscal situation in Ukraine, the Russian Central Bank cut its policy rate by 150bps to 8.0%, against consensus for a 50bps cut to 9.0%, and signalled it was willing to cut the rate further over the next months. Russian PPI inflation dropped 4.1% in June after declining 6.9% in May due to a strong performance of the RUB, bringing the yoy rate of PPI inflation down 800bps to 11.3%.
In other geopolitical news, Japan said Russia and China’s deepening military cooperation is raising security concerns in the region and for Taiwan.
Emerging markets
Argentina: The trade balance moved to a USD 115m deficit in June from a USD 356m surplus in April, significantly below consensus as imports accelerated by USD 700m to USD 8.55bn and exports rose USD 200m to USD 8.4bn. The central bank announced two measures to improve net FX reserves which stood below USD 3bn last week. Tourists will be allowed to sell up to USD 5k in the official market at the free exchange rate, now 150% higher than the official rate and foreign stocks will be included in the current USD 100k limit to hold liquidity abroad for companies in an attempt reduce the fraction of businesses’ foreign assets and get positive inflows in the parallel exchange market.
Brazil: Tax collections rose to BRL 181bn in June from BRL 165bn in May, surprising consensus to the upside. The National Treasury reported government debt is declining and expected to end the year at 78.3% of GDP. Debt should keep declining through the end of the decade, assuming a constant 1.2% primary surplus, whilst the same report a year ago projected debt at 100.5% of GDP by 2025. The state-owned oil company Petrobras cut gasoline prices by 4.9% to BRL 3.86 per litre, bringing local prices in line with international markets, but kept diesel prices unchanged, which means diesel prices are now higher in Brazil than abroad.2
Chile: President Gabriel Boric pledged to restart the constitutional referendum process if the new constitution written by the Constitutional Assembly is rejected in September. Boric is distancing himself from a constitution that is likely to be rejected, while keeping his raison d'etre of reforming the country’s welfare state. The government unveiled a tax reform plan intended to gradually raise taxes by more than 4.0% of GDP by 2026 by gradually increasing income tax, royalty for mining, levying a wealth tax and fighting tax evasion. The tax increases are aimed at funding an ambitious spending programme including pensions, healthcare, and infrastructure investment. The tax reform is likely to be watered down, which would be good news if welfare spending is cut pro-rata. A poll by Caden shows 58.4% of the population rejected the new constitution while 41.6% approve it. Another poll by Activa shows 29.5% of the population approves of the Gabriel Boric administration while 57.7% disapproves of him.
China: Tech Insights reported SMIC is shipping 7nm semiconductors for bitcoin mining, two generations ahead of the stablished 14nm technology it current possesses. Similar reports were published over the last few years but proved to be incorrect. If confirmed, China will have achieved an important technological break-through despite tight restrictions imposed by the US on exports of high technology semiconductors machinery and components to China. However, China remains behind the curve in the semiconductor industry with TSMC working on 3nm prototypes.
Real estate companies staged a recovery this morning after reports that China Construction Bank is setting up a fund alongside a few local governments to buy unsold projects under construction. According to REDD, the fund secured RMB 50bn (USD 7.4 bn) from China Construction Bank Corp. and a RMB 30bn re-lending facility from the People’s Bank of China. The report mentioned the fund can be scaled up to between RMB 200bn and RMB 300bn.
In other news, several media outlets published pictures of tanks on the streets of Henan protecting banks against angry crowds. The protests in Henan are two months old as many individuals were victims of an embezzlement fraud where a company offered what appeared to be an online deposit product from large province banks and stole the monies. When the banks said they could not “repay” money they never received, the fraud victims took to the streets and last week the military was sent to protect some branches. The local government is stepping up to support the small depositors (up to RMB 50k), but larger depositors are on the hook to lose their capital. As of today, only four regional banks were involved in embezzlement fraud schemes. There are four-thousand regional banks controlling USD 14trn of assets in China.
Colombia: Economic activity rose by 16.5% yoy in May from 11.9% yoy in April, slightly below consensus. Strong demand boosted imports by USD 400m to USD 6.8bn in May, leading to a widening of the trade deficit to USD 1.7bn in May from USD 0.5bn in April. Central Bank Governor Villar noted neutral rates are likely rising from the current 1.9% estimate by staff and noted that real rates above neutral are necessary, suggesting another 150bps hike is possible in this week’s monetary policy committee meeting.
Ecuador: Ecuadorian bonds rebounded more than 10 points last week after the government struck a deal with the indigenous leaders whereby public and private banks will provide USD 540m in credit, including USD 120m for loans and investments to credit and savings cooperatives, and USD 120m in microcredits from state development bank CFN. President Guillermo Lasso vetoed a labour law bill that included a series of debt condonation measures as he said 112k jobs would be at risk, that debt condonation measures are the Executive’s responsibility and were already negotiated with indigenous groups.
Indonesia: Bank Indonesia (BI) kept its policy rate unchanged at 3.5%, in line with consensus, keeping its strategy of mopping up liquidity through monetary operations as inflation expectations remained anchored within BI’s 2-4% target range. President Joko Widodo will meet with his counterpart Xi Jinping and Premier Li Keqiang today and tomorrow in Beijing for an “an in-depth exchange of views focusing on bilateral relations and major regional and international issues”, the first visit to China by a foreign leader since the Winter Olympics in February.
Mexico: The United States said it would seek dispute talks with Mexico over energy policies infringement of the USMCA Free Trade Agreement. Trade Chief Katherine Tai said: "We have repeatedly expressed serious concerns about a series of changes in Mexico's energy policies and their consistency with Mexico's commitments under the USMCA trade deal”. Mexico would be liable for as much as USD 30 billion in tariffs if it loses the dispute with the US and Canada, according to two former officials who negotiated the USMCA agreement. In other news, CPI inflation was unchanged at 0.4% mom in the first 15 days of July, taking the yoy rate up 10bps to 8.2%, while core CPI rose 0.3% mom and 7.6% yoy over the same period. retail sales rose another 0.5% mom in May after increasing 0.4% mom in April, bringing the yoy rate up 60bps to 5.2%.
Pakistan: The ratings agency Fitch revised Pakistan’s sovereign rating outlook to negative and maintained its `B-` rating. The Pakistan Rupee dropped 8.3% last week, the largest decline since 1998, adding pressure on the country’s external payments. The country was hit by higher bill for food and energy imports after taking too long to unwind subsidies, leading to a large drawdown in FX reserves. A large and credible fiscal consolidation could backstop the vicious market cycle dynamics, including the rout on the PKR, but it is challenging to implement at the current political juncture. Pakistan has USD 7.8bn of Eurobonds (USD 1.0bn due in Dec 2022) and USD 15.2bn of FX reserves (down from 27.2bn in August 2021). At current market prices, the country could spend 5% of its FX reserves (USD 0.75bn) to buy back more than USD 1.5bn of Eurobonds (c. 20% of outstanding). The measure would only have a sustained effect if, in parallel, it announced a large primary surplus target for the 2022/23 budget alongside an IMF deal and bilateral support. The measures could be successful in backstopping the vicious spiral where high inflation led to higher levels of local currency yields and weaker currency, which increases indebtedness, leading to poor sentiment and even weaker currencies.
South Africa: The reserve bank of South Africa hiked its policy rate by 75bps to 5.75%, 25bps above consensus. Two out of five voting members of the monetary policy committee dissented, with one voting for a 50bps hike and another for a 100bps hike. The yoy rate of CPI inflation rose 90bps to 7.4% in June as core CPI rose 30bps to 4.4% over the same period.
Uruguay: President Luis Lacalle Pou said Uruguay will meet China in a few days to start negotiations for a free trade agreement. Uruguay is threatening to break out of the Mercosur free trade zone (Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, and Paraguay) if no consensus is reached for a broad deal between the South American block and China. Last Wednesday the Mercosur concluded a free trade agreement with Singapore that would boost exports by about $500 million a year from $5.9 billion in 2021.
Zambia: President H. Hichilema said his government will reach a deal with official creditors within days that could unlock a USD 1.4 bn IMF programme aimed at improving the country’s fiscal accounts. The IMF could also provide guidance and assurance to a debt restructuring with Eurobond holders.
Snippets
Croatia: The ratings agency Moody’s upgraded Croatia’s sovereign credit rating to `Baa2`, keeping the rating one notch below S&P and Fitch at BBB+.
Czechia: The yoy rate of PPI inflation rose 60bps to 28.5%, marginally below consensus.
Egypt: The trade deficit widened to USD 2.6bn in May from USD 1.7bn in April. The General Authority for Supply Commodities (GASC) purchased 640k tons of wheat in private negotiations, mostly from France as well as Russia, Germany, and Lithuania at USD 403 per ton, more than 20% lower than the levels in April.
Ghana: FX reserves declined to USD 7.6bn in June, equivalent to 3.4 months of imports, from USD 8.1bn in May. Parliament approved a USD 750m loan from Afrexim Bank.
Malaysia: The yoy rate of CPI inflation rose 60bps to 3.4% in June, 20bps above consensus, while core inflation reached 3.0% yoy, the highest level since April 2016. The trade surplus improved to MYR 21.9bn in June from MYR 12.7bn in May as exports rose by a yoy rate of 38.8% and imports by 49.3%
Nigeria: The Central Bank of Nigeria raised its policy rate by 100bps to 14.0%, significantly above the 25bps consensus.
Poland: Core CPI inflation moderated to 0.6% mom in June from 1.0% mom in May, but the yoy increased 60bps to 9.1% due to base effects but PPI inflation rose 1.6% mom from 1.4% over the same period bringing the yoy rate up 90bps to 25.6%. Construction sold, industrial output and retail sales were weaker than consensus expectations.
South Korea: Export growth for the first 20 days of July rose by a yoy rate of 14.5% as imports increased 25.4% yoy.
Taiwan: Export orders rose by a yoy rate of 9.5% in June from 6.0% yoy in May.
Turkey: The Central Bank of Turkey kept its policy rate unchanged at 14.0%, in line with consensus. Erdogan said that US forces should leave the east of Euphrates River, as it pushes its campaign against Kurdish people in Northern Syria, a campaign supported by Russia.3
Global backdrop
United States: Housing market leading indicators are declining sharply. The National Association of Home Builders Market Index dropped by 12 points to 55 in June, from 84 in December 2021, the third sharpest drop in 30 years after the 76 to 30 plunge from Dec 2019 to April 2020 and the 72 to 8 decline from May 2005 to Jan 2009. Mortgage applications dropped to the lowest level since 2000. Coincident indicators are deteriorating, albeit at a slower pace: home sales dropped 5.4% mom in June after -3.4% in May, housing starts dropped 2.0% mom in June after declining 11.9% in May and building permits dropped 0.6% mom in June after 7.0% in May. The Philadelphia Fed Business Outlook survey dropped another 9.0 points to -12.3. The labour market is starting to feel the slowdown as several companies reported hiring freezes or layoffs and initial jobless claims rose to 251k in the week of the 16 July from 244k in the previous week as continuing jobless claims increased to 1.38m in the 9 July week from 1.33m previously.
United Kingdom: Employment jumped to 296k on a 3m/3m basis in May vs 177k in April, but unemployment rate was unchanged at 3.8%, in line with consensus, and weekly earnings slowed to 6.2% yoy from 6.8% previously. CPI inflation rose by 0.8% mom in June after 0.7% in May, taking the yoy rate up 30bps to 9.4% as core CPI declined 10bps to 5.8% yoy over the same period.
Europe: The European Central Bank hiked its policy rates by 50bps, bringing deposit banks to 0.0% and lending rates to 0.5% and announced a third mechanism to backstop peripheral countries’ yields widening called Transmission Protection Instrument (TPI). The TPI will purchase one to 10-year bonds from a country whose yield curve is widening significantly, contingent on four discretionary conditionalities: (1) compliance with the EU fiscal framework; (2) no severe macroeconomic imbalances; (3) fiscal sustainability, and (4) sound and sustainable macroeconomic policies.4 Instead of expanding the ECB balance sheet, the TPI would sell bonds from core countries to fund the purchase of peripheral countries. The programme acts like a disguised fiscal transfer mechanism as the ECB balance sheet will act as a backstop and increase the exposure in countries with higher funding costs, should market volatility increase significantly. The objective of the programme is to allow a smooth transmission mechanism of monetary policy across the Eurozone. The ECB decision happened one day after former ECB Governor Mario Draghi resigned as prime minister of Italy after not having his conditions met to remain in power. Italy is very much in a grey area in at least three out of the four conditions, particularly against a backdrop of fresh elections on 25 September. The ECB press conference did not help to clarify whether Italy was eligible to the programme, but Italian yields declined after the European Flash PMIs came at recessionary levels in July. Economic data was very weak across the Eurozone with the Citibank Surprise index dropping to -92.2, the lowest level since May 2020 and consistent with the low readings after the strong slowdown caused by the banks-sovereign debt crisis in 2011-12. Eurozone consumer confidence declined to -27.0, the lowest level since 1983.
Japan: The Bank of Japan kept its policy rate unchanged at -0.1% and the yield target on 10-year Japanese Government Bond (JGB) at 0.0%. The BOJ increased its Q3 2022 CPI inflation forecast to a yoy rate of 2.3% but expects inflation to decline to 1.4% and 1.3% in the subsequent quarters as GDP growth projections were revised lower to 2.4% yoy in Q3 2022, 2.0% and 1.3% over the next quarters.
Australia: The Reserve Bank of Australia sees the current policy rate (at 1.35%) “well below the lower estimates of neutral” and recognised the need to keep tightening policy.
Canada: The yoy rate of CPI inflation increased 40bps to 8.1% in June, 30bps below consensus.
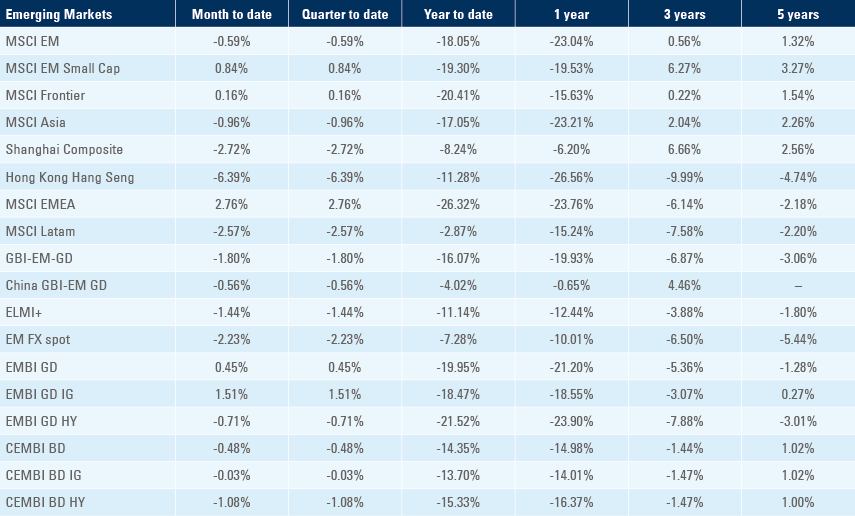
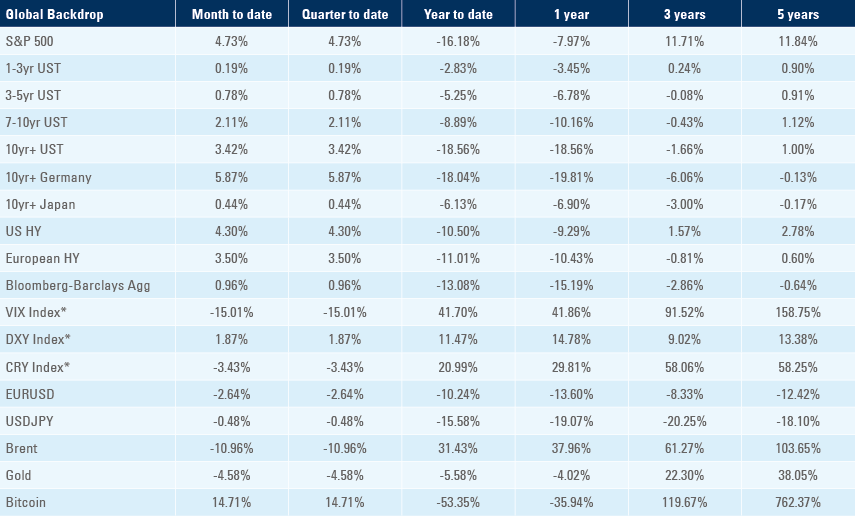
Benchmark performance
1. See https://blinks.bloomberg.com/news/stories/RFF2X9T0AFB4
2. See https://abicom.com.br/ppi/ppi-25-07-2022/
3. See https://www.aa.com.tr/en/middle-east/russia-keeps-strengthening-its-existence-in-ne-syria-east-of-euphrates-river/2630167
4. See https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2022/html/ecb.pr220721~973e6e7273.en.html