
Chileans reject new constitution and Europe faces an energy crisis
European energy prices remain elevated as Gazprom shuts down the Nord Stream 1 pipeline. The manufacturing PMIs again showed for a much more resilient picture across Emerging Market countries. Chileans rejected the new constitution. China grapples with rolling lockdowns in two large cities. Brazil economic data surprised to the upside again. South Korea had mixed data as the trade deficit widened. The IMF approved a USD 2.9bn bail-out programme to Sri Lanka.
Geopolitics and commodities
The finance ministers of the group of seven largest economies in the world (G7) agreed to set a price cap mechanism on energy exports from Russia, with the intention to limit the capacity of Russia to monetise high energy prices while guaranteeing the availability of energy at a low cost for low-income countries.1 British insurance companies, responsible for 95% of all shipping insurance in the world, will not be allowed to insure shipments from Russia above the price limit, to be set and announced after consultations with an “extensive group of countries and key stakeholders”. All 27 members of the European Union (EU) must implement the measure in their own jurisdictions.
One day after the price cap announcement, and amidst the strongest Ukrainian counter-attack since the beginning of the conflict, Gazprom shutdown the entire gas flow from the Nord Stream 1 pipeline after scheduled maintenance, blaming oil leaks for the interruption. Europe managed to build the gas in storage to 82.9% of capacity, which is close to the 90% level required for Europe to survive an average temperature winter, assuming some demand replacement and high levels of liquified natural gas (LNG) imports. However, the margin of safety has been dramatically reduced as Russia is now sending only c. 11% of the flow it sent to Europe at its peak across the three main pipeline systems and 18.5% of 2021 average. The president of the German Federal Network Agency energy regulator Klaus Mueller said that even with 95% of storage full, there would be enough for only 2.5 months of demand, should Russia switch off flows. Gazprom said it would increase the shipments of gas to Europe via Ukraine. In theory, the Ukrainian pipeline is running at only 20% capacity, but there is no reason to believe Russia will de-escalate the crisis.
Sweden set up a EUR 23bn emergency backstop for utilities while Germany announced EUR 65bn to help households struggling with soaring prices as European natural gas hit 5x the level of oil prices (in energy equivalent terms). Faced with the risk of energy rationing and blackouts in the winter, Europe will discuss more radical energy intervention tools in a meeting next Friday. Possible measures include to cap temporarily the price of gas used for electricity generation, putting a price ceiling on gas imported from Russia, and temporary exclusion of power production from gas. On the liquidity side, an EU-wide credit line support for market participants faced with high margin calls and a temporary suspension of EU power derivatives markets is being considered.
Dozens of Chinese civilian drones flew over the Taiwanese territory several times last week. The Taiwanese army retaliated striking one of them down. The provocation seems to be intended to create a sense of normality of Chinese incursions on its neighbour island.
Purchasing Managers Index
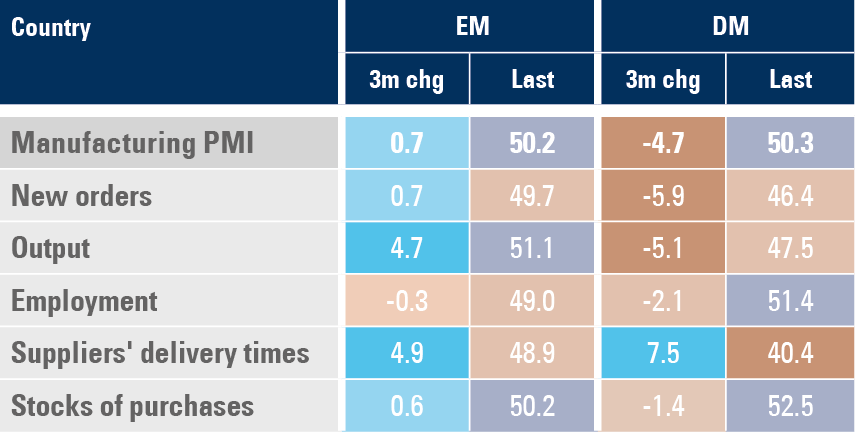
The manufacturing PMI declined 0.8 to 50.3 with EM down 0.6 to 50.2 and DM down 1.0 to 50.3. Figure 2 depicts the level of activity reported by the survey and the breakdown across subcomponents. Notably, EM PMI remained on an upward trend over the past three months with current output still above 50-levels, contrasting with the strong decline in new orders and output in DM PMIs.
Figure 1: Manufacturing PMI: DM vs EM
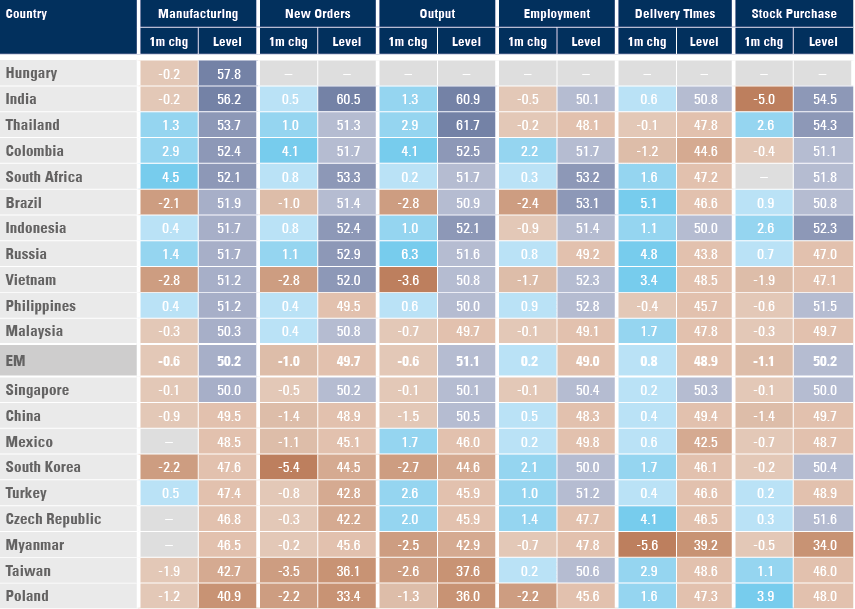
Within EM, the manufacturing PMI improved the most in South Africa, Colombia, Russia and Thailand as new orders and output remained above 50.0 across most countries. The PMIs deteriorated in key manufacturing hubs of Vietnam, South Korea, and Taiwan as well as Brazil as per figure 3. The Chinese manufacturing PMI declined 0.9 to 49.5, the main contributor to the decline in the EM PMI index.
Figure 2: EM PMIs by country
Emerging markets
Brazil: Real GDP growth rose to 1.2% qoq in Q2 2022 from 1.1% in Q1, bringing the yoy rate up 150bps to 3.2% over the same period, 40bps better than consensus. The strong activity data led several economists to review their 2022 GDP growth forecast to between 2.5% and 3.5% last week from only 0.5% in Q1 2022. Formal job creations softened to 219k in July from 279k in June, 40k less than consensus. The trade surplus narrowed to USD 4.2bn in August from USD 5.4bn in July but was better than USD 3.6bn consensus as exports rose USD 0.8bn to USD 30.8bn and imports increased USD 2.2bn to USD 26.7bn. The ratio of net debt to GDP dropped 50bps to 57.3% in July, 150bps below consensus and 5.2% below its peak in December 2020 as the nominal fiscal deficit improved to BRL 22.5bn in July from BRL 83.8bn in June, also better than expected. PPI inflation declined 0.7% mom in August after rising 0.2% in July, bringing the yoy rate down 150bps to 8.6% over the period. Inflation is likely to keep declining as Petrobras cut gasoline prices again last week by 7.6%, which should have a 20bps impact on CPI in 2022.
Chile: Chileans rejected the new constitution drafted by a Constitutional Assembly with 61.86% of the population rejecting the new document and 38.14% approving. Copper production declined to 430k tons in July from 462k tons in June, the lowest production level for the month in 10-years. The yoy rate of economic activity index slowed to 1.0% in July from 3.3% in June (revised from 3.7%), as industrial production dropped 5.1% and retail sales dropped 10.9% over the same period, both below consensus.
China: The large cities of Chengdu and Shenzhen (each with a population of more than 15m) adopted lockdowns after a spike in cases forced authorities to adopt a more stringent mobility. The official National Bureau of Statistics manufacturing PMI improved 0.4 to 49.4 in August, but service PMI declined 1.2 to 52.6 over the same period, both slightly better than consensus.2
South Korea: The yoy rate of real GDP growth rose 2.9% in Q2 2022, unchanged from Q1 2022 and in line with consensus. CPI inflation declined 0.1% mom in August from +0.5% in July, bringing the yoy rate down 60bps to 5.7%, or 40bps below consensus. Industrial production declined 1.3% mom in July after rising 1.7% in June, bringing the yoy rate 20bps higher to 1.5%, as retail sales rose 50bps to 9.7% yoy in July and department store sales rose to 31.6% yoy from 19.0% in June. The trade deficit widened to USD 9.5bn in August from USD 4.8bn in July as higher energy prices increased imports and a strong slowdown in exports of electronic goods led to lower exports.
Mexico: Unemployment rate was unchanged at 3.4% in July, 10bps below consensus. Foreign exchange remittances rose to USD 5.3bn in July from USD 5.15bn in June, setting a record level that is 16.5% higher than the same period in 2021 and 50.0% above the same levels in 2020. Domestic vehicle sales improved to 91.1k units in August from 83.1k in July, remaining 12.0% below the average of the past five years.
Vietnam: The trade surplus rose to USD 2.4bn in August as exports rose by a yoy rate of 22.1% (up from 8.9% in July) to USD 33.4bn and imports increased 12.4% yoy (up from 3.4%). Industrial production rose by a yoy rate of 15.6% from 11.2% in July and retail sales surged 50.2% from 42.6% over the same period. Despite the buoyant economic growth, CPI inflation declined 25bps to 2.9% yoy.
Sri Lanka: IMF approved a USD 2.9bn bail-out program. The programme is conditional upon strict conditionalities, including a smaller fiscal deficit than approved by the government as well as bilateral and multilateral debt restructurings. The key questions are whether local debt will be restructured and if China will accept similar conditions than other bilateral creditors and Eurobond holders on the debt restructuring. China so far has accepted to reprofile the debt with low-income countries, including Ecuador, Angola and Zambia, which in most cases paved the way for a comprehensive debt reprofiling which allowed multilateral institutions such as the IMF to lend money to the country.
Snippets
- Argentina: Vice President Cristina Kirchner was assaulted by a gunman but escaped unharmed.
- Colombia: The current account deficit was unchanged at USD 5.0bn in Q2 2021, USD 1.0bn wider than consensus. The national unemployment rate improved 30bps to 11.0% in July as the urban unemployment dropped by 40bps to 11.3% over the same period.
- Czech Republic: The yoy rate of GDP growth rose 10bps to 3.7% in Q2 2022, slightly above consensus.
- Hungary: The central bank hiked its policy rate by 100bps to 11.75%, in line with consensus, as PPI inflation rose another 5.7% mom in July bringing the yoy rate up 290bps to 37.9%.
- India: The yoy rate of GDP growth surged to 13.5% in Q2 2022 from 4.1% in Q1 2022, slightly below consensus.
- Indonesia: CPI inflation dropped 0.2% mom in August, 10bps more than consensus, from 0.6% in July, bringing the yoy rate down 20bps to 4.7% as core CPI rose 10bps to 3.0% yoy over the same period.
- Malaysia: The yoy rate of CPI inflation rose 100bps to 4.4% in July, in line with consensus.
- Mongolia: Rio Tinto announced it will take full control of Turquoise Hill, buying the 49% of the company that it does not own from a Canadian company for USD 4.85bn. Chief executive Jakob Stausholm said the deal will simplify governance and create greater certainty of funding for the Oyu Tolgoi project. The Turquoise Hill shareholders meeting to approve the transaction is expected to be held in early Q4 2022.
- Peru: CPI inflation in the city of Lima declined to 0.7% mom in August from 0.9% in July, bringing the yoy rate down 30bps to 8.4% over the same period.
- Poland: The yoy rate of real GDP growth improved to 5.5% in Q2 2022 from 5.3% in Q1 2022 and CPI inflation rose 0.8% mom in August from 0.5% in July, taking the yoy rate up 50bps to 16.1%.
- Romania: PPI inflation rose 5.2% mom in July from 3.1% in June, bringing the yoy rate up another 420bps to 52.3%. The unemployment rate declined 20bps to 5.2% over the same period.
- South Africa: The fiscal accounts deteriorated to a ZAR 130bn deficit in July from a ZAR 74bn surplus in June, slightly more than usual seasonal patterns and the trade surplus improved marginally to ZAR 24.8bn in July, slightly better than consensus.
- Thailand: The current account deficit widened to USD 4.1bn in July from USD 1.9bn in June as the trade balance moved to a USD 400m deficit from a USD 2.1bn surplus over the same period.
- Turkey: The yoy rate of real GDP growth improved to 7.6% in Q2 2022 from 7.5% in Q1 2022, better than consensus as the trade deficit widened to USD10.7bn in July from USD 8.2bn in June, in line with consensus.
Developed markets
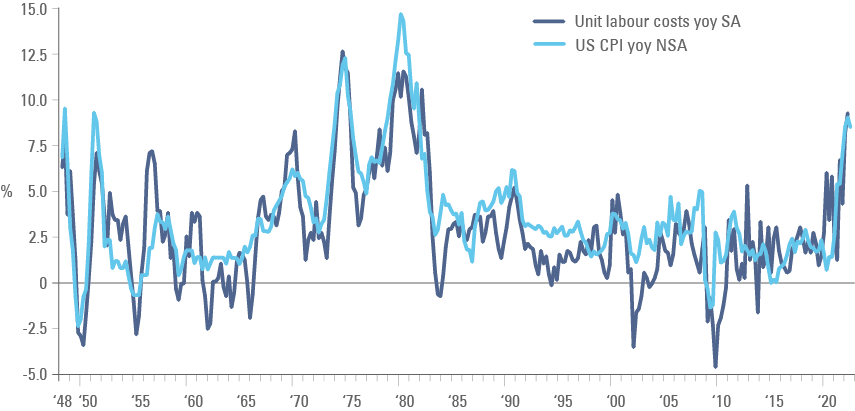
United States: Economic data was overall stronger than expected. In the labour market, non-farm payrolls increased 315k in August from 526k in July, the unemployment rate rose 20bps to 3.7% due to a 0.3% increase in the labour force participation rate to 62.4%, and average hourly earnings growth level was unchanged at 5.2%. Similarly, job openings on the JOLTS report improved to 11.2m in July from 11.0m in June, almost 1m above consensus, remaining at the most elevated level in history, but the ADP employment change declined to 132k in August from 268k in July (below 300k consensus). Unit labour cost by the labour bureau of statistics increased at a yoy rate of 9.3% in Q2 2022 from 8.2% in Q1 2022, the fastest rate since the 1970-1982 period as per figure 4, while productivity declined by 2.4% yoy, the fastest rate of decline in history.
Figure 3: Unit Labour Cost vs. CPI
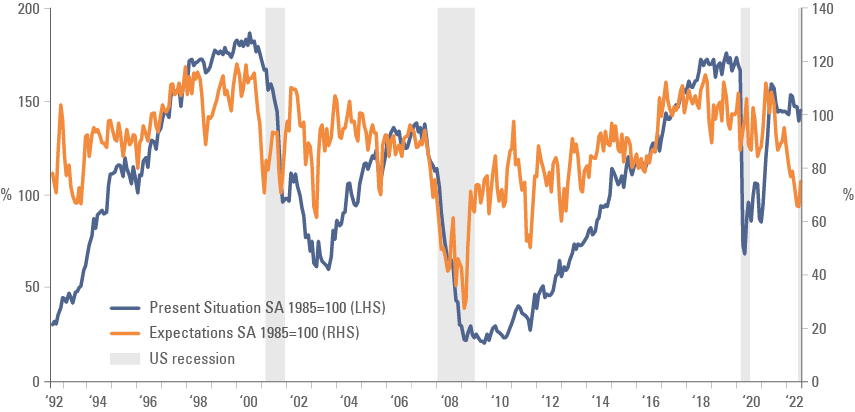
In other news, the Institute of Supply Management (ISM) manufacturing index was unchanged at 52.8 (consensus 51.9) but with a much better breakdown as prices paid declined 7.5 to 52.5, new orders rose 3.3 to 51.3 and employment increased 4.3 to 54.2. The Dallas Fed manufacturing activity index improved 10 points to -12.9 in August, in line with consensus. Consumer confidence improved 7.9 points to 103.2 in August, with both present situation and expectations recovering, but with the latter remaining on a declining trend as per figure 5. Factory orders dropped 1.0% in July after rising 1.8% in June as durable goods orders declined 0.1% in July (stable in June).
Figure 4: US Conference Board Consumer Confidence
Europe: CPI inflation rose 0.5% mom in August, increasing the yoy rate by 20bps to 9.1% as core CPI rose 30bps to 4.3%. PPI inflation rose 190bps to 37.9% in July, 60bps above consensus and the unemployment rate was unchanged at 6.6% over the same period.
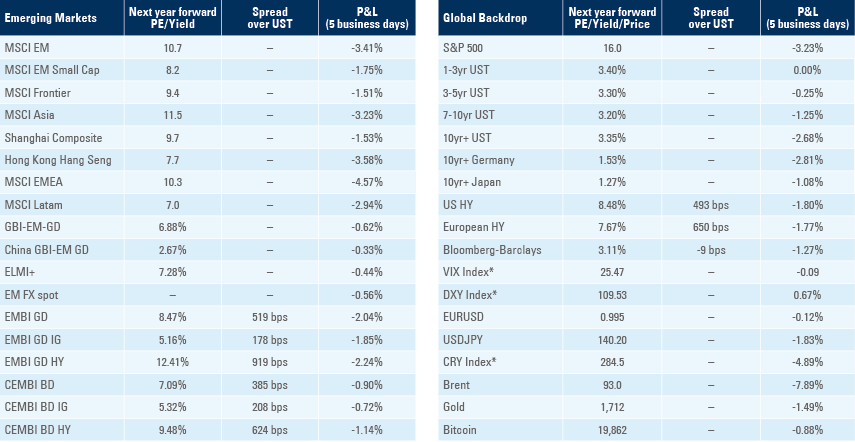
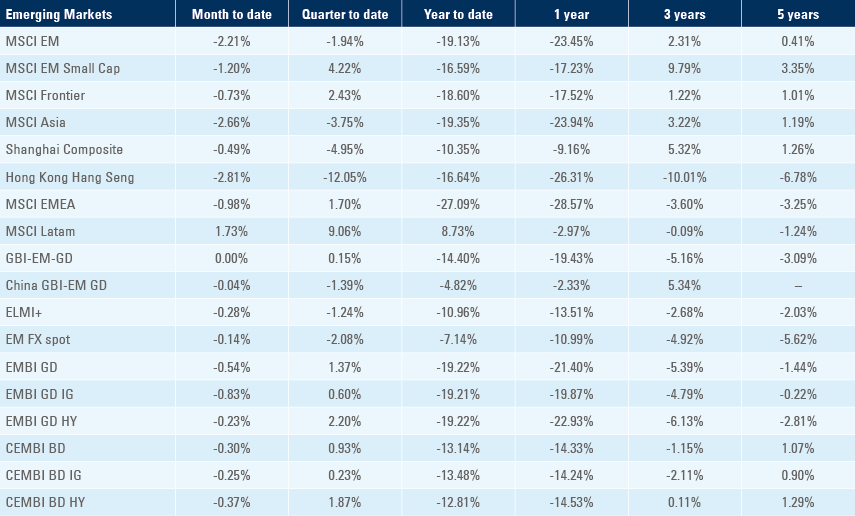
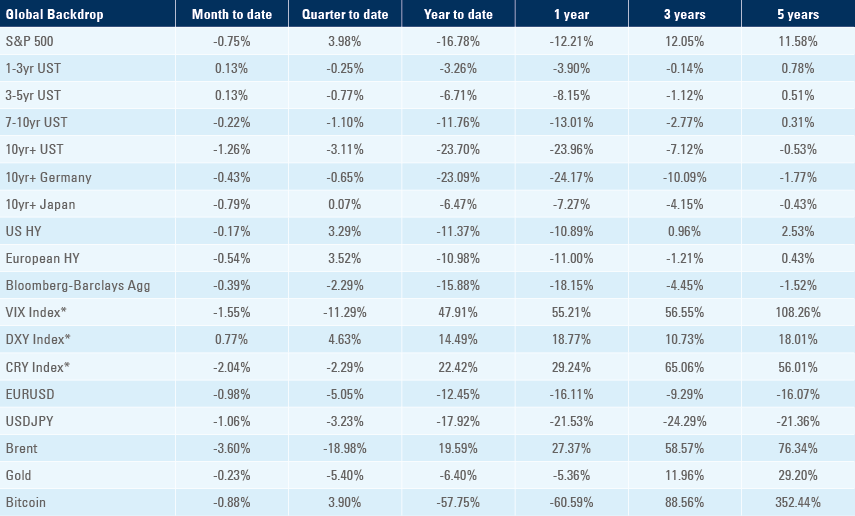
Benchmark performance
1. See https://www.gov.uk/government/news/g7-finance-ministers-statement-on-russias-war-of-aggression-against-ukraine
2. The NBS Purchasing Manager’s Index is collated by the China Federation of Logistics using a larger sample of 3k companies across different sectors.