
- US macro data continues to point to a ‘goldilocks’ scenario, with inflation falling further.
- The correlation between the Japanese yen and Japanese stocks flipped positive.
- AI-led fears continue to weigh on risk sentiment, but EM stocks are holding up very well.
- Republican Senator Thom Tillis said he had not made a deal on Kevin Warsh’s Fed confirmation.
- President Lula’s approval rating fell to 45% in February.
- Colombia’s presidential race remains highly competitive.
- Moody’s affirmed El Salvador’s ‘B3’ rating and revised the outlook to positive.
- Mexico’s central bank held its policy rate at 7.00% and reiterated a dovish bias.
- Angola’s first copper and cobalt shipment was delivered via the Lobito Atlantic Railway.
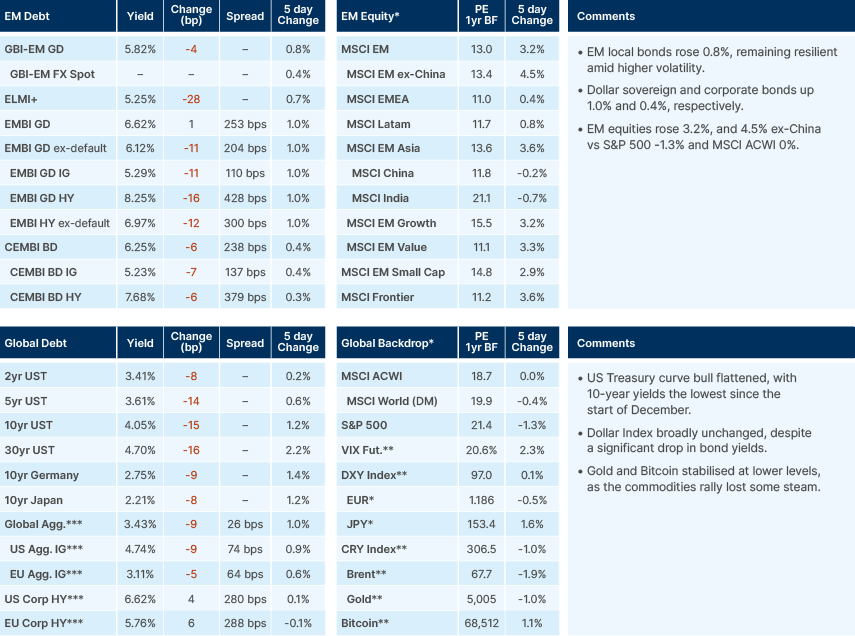
Last week performance and comments
Global Macro
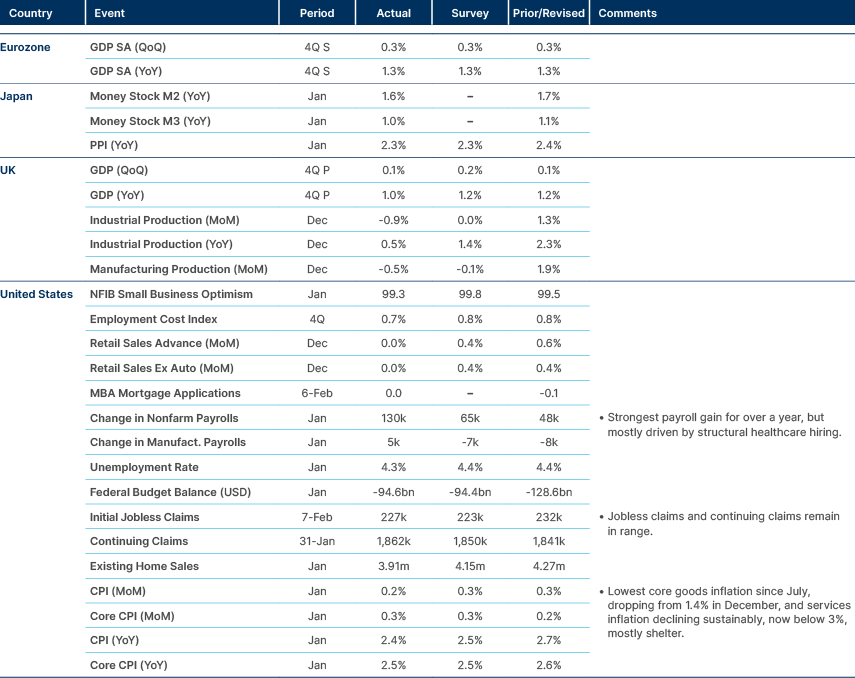
US macro data releases last week continued to point towards our base case of a ‘goldilocks’ macroeconomic environment of sustained growth, but lower inflation and lower rates in 2026. US payrolls were the strongest in over a year, with 130k jobs added to non-farm payrolls (NFP) in January. This brings the three-month moving average (MA) of payrolls into positive territory. These numbers quell fears of a quick deterioration in employment dynamics. But this is not a strong labour market. Almost all payroll growth continues to come from the healthcare sector, reflecting ageing demographics rather than underlying economic strength. Ex-healthcare and education, payroll growth has remained negative; -7k in January, -9k on a three-month MA basis, and -47k on a six-month MA. Revisions to prior NFP data continued to be show heavy downside. Now, total revisions show just 181k of job creation in 2025 versus 584k last reported. This is the worst non-recessionary year for jobs creation since 2003. The reason unemployment has not risen faster is due to US President Donald Trump’s immigration policies. Our base case – that further artificial intelligence (AI)-related job destruction this year will lead to more rate cuts than expected – holds. The market is still fully pricing just two cuts by the end of the year.
Looking at the other side of the US Federal Reserve (Fed)’s dual mandate, consumer price index (CPI) inflation is also falling faster than expected this year, after surprising to the downside again last week. Headline CPI inflation fell to 2.4%, driven largely by the continuation of housing disinflation. Shelter inflation is now running at 3.0%, down from 4.4% this time last year. The trend for housing inflation continues to point steadily lower. Core services inflation (of which housing is 70%), has now fallen to 2.9%, the lowest since October 2021. Core goods inflation seems to have peaked at levels far lower than most expected, given tariffs. Having risen to 1.4% in December, core goods inflation fell in January to 1.1%. The ‘Truflation’ indicator has now fallen to 0.9%, which suggests further downside to CPI inflation in coming readings.
Last week, for the first time since 2005, the correlation between the Japanese yen and the Japanese stock market flipped positive. Historically, this has been a leading indicator for a secular bull market driven more by domestic-led growth rather than export demand. In the near term, however, the Yen appreciating could lead to a further unwind of the Yen carry trade. A sharp, disorderly appreciation of the Yen would likely tighten global financial conditions, as episodes of rapid JPY strengthening have historically coincided with broad-based deleveraging and a contraction in global liquidity.
AI-led fears continue to weigh on risk sentiment. The S&P 500 failed to sustain a break above 7,000 again. Friday saw further rotation out of US large-cap tech, as investors trimmed exposure amid valuation concerns and heightened volatility around the AI theme. Software stocks became the new focus of concern after the abilities of Anthropic’s newest Claude model surpassed expectations and put to bed any opinions that AI progress is slowing down. In relative value terms (price/earnings) US software stocks (S&P North American Expanded Technology Software Index) versus the S&P 500 peaked in 2021 and now have fully converged. Emerging market (EM) software stocks (MSCI EM Software & Services index) peaked relative to the MSCI EM at around the same time but still trade at a premium.
Overall, the S&P 500 has been stuck in a 6800-7000 range over the last two-months, while correlation between index members has been falling. While the S&P 500 has been treading water YTD (-0.1%) MSCI EM equity outperformance continues apace, now 12% YTD. MSCI EM was up 3.2% last week, driven by Asia ex-China tech, while the S&P 500 fell 1.2%. The ‘AI trade’ was the primary reason for both moves – a demonstration, in our view, that the market increasingly sees EM stocks as a clear ‘winner’ of AI capex amid ongoing concerns around the profitability of the capex for US hyperscalers.
In other news, Republican Senator Thom Tillis said he had not made a deal on Kevin Warsh’s confirmation as the next Fed Chair. In an interview with CBS, Tillis said he stood by his assertion he will not vote for Warsh until the legal case surrounding current Chair Jerome Powell has been dealt with. Note, his comments to CBS were a push back to those of Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent on Friday, who said he expected Warsh to move to a confirmation hearing soon. Bessent said an agreement had been reached with a group of senators to advance Warsh.
Commodities
European natural gas prices have pulled back from recent highs even as storage levels remain uncomfortably low for this point in the season, which looks counterintuitive on the surface. The main driver is that near-term balance risks have eased: milder weather reduced heating demand, industrial consumption remains subdued, and LNG inflows have been steadier than feared, limiting the urgency bid that typically appears when inventories look tight. With the front of the curve less stressed, prices have softened even though the underlying buffer is thin.
That said, low storage still matters for risk premia and for next season’s refill economics. A smaller end-winter inventory position raises the volume Europe will need to buy through spring and summer, and if global LNG supply is disrupted or Asia competes more aggressively for cargoes, the market can reprice quickly. The current pullback therefore looks more like a pause driven by improved short-term fundamentals and positioning than a clean resolution of the structural tightness, leaving European gas prices vulnerable to weather volatility and any supply shocks.
Emerging Markets
Asia
Inflation remains close to zero in China and very low in India.
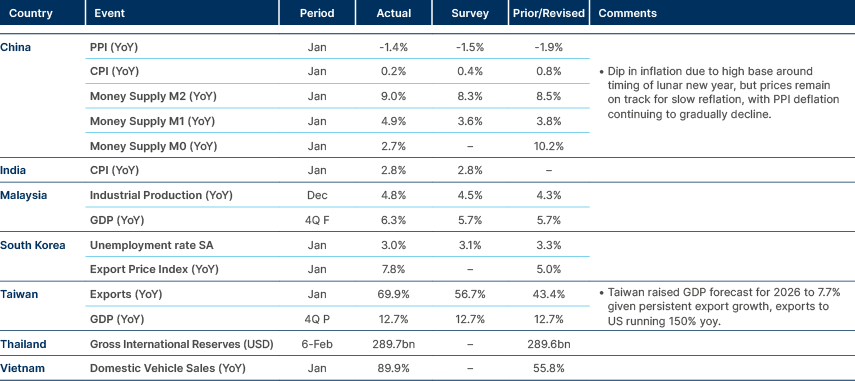
China: Chinese tech stocks briefly sold off after the Pentagon momentarily listed Alibaba, Baidu and BYD as firms aiding China’s military, before withdrawing the “unpublished” register minutes later. The episode highlights how a 1260H designation, though carrying limited immediate legal impact, is seen as a warning flag that can precede tighter restrictions.
Pakistan: Moody’s revised the banking sector outlook to stable from positive, citing only gradual improvement in the operating environment and continued close sovereign linkages (‘Caa1’/stable). Banks remain heavily exposed to government securities, which account for around 50% of total assets, with the advance-to-deposit ratio at a low 39.8% as of December 2025 and the investment-to-deposit ratio at 101.3%. Tier 1 and total capital ratios stood at 18% and 22.1%, respectively in September 2025, well above regulatory minima. Private credit growth is projected to remain in double digits in 2026 after 10.7% growth in 2025. Moody’s expects GDP growth to accelerate to 3.5% in 2026 (from 3.1% in 2025), while inflation is forecast to rise to 7.5% from a nine-year low of 4.5%, partly due to base effects.
South Korea: Samsung announced mass production of sixth-generation HBM4 memory chips, becoming the first global producer to do so. The chips reportedly passed Nvidia’s quality tests ahead of schedule, positioning Samsung to overtake SK Hynix in technological leadership in the high-bandwidth memory segment. The company expects HBM sales to triple in 2026 compared to 2025, supported by strong AI-related demand. The move reinforces South Korea’s strategic position in advanced semiconductor supply chains.
Latin America
Inflation increasing sequentially in Argentina; uptick in inflation in Mexico and Brazil.
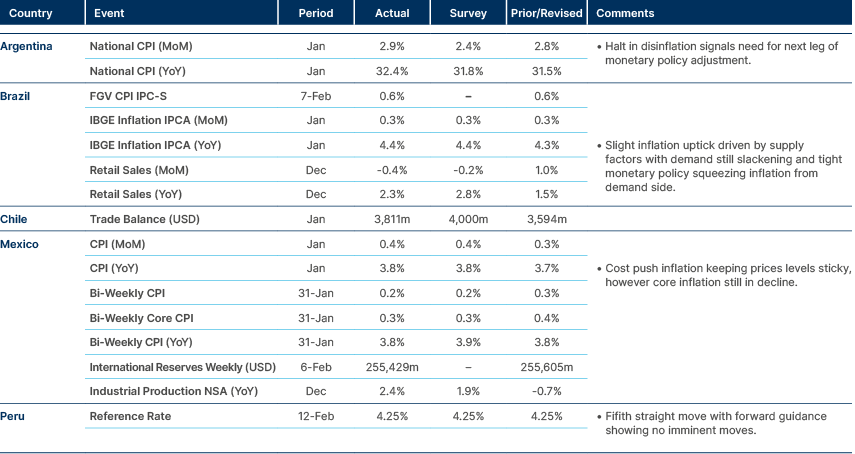
Brazil: President Lula’s approval rating fell to 45% in February from 47% in January, while disapproval held at 49%, according to a 5–9 February Quaest poll. Despite the decline, Lula remains the frontrunner for the October election in all tested scenarios. In a runoff against Flavio Bolsonaro Lula’s lead margin narrowed to 5% from 7% previously. Economic perceptions remain weak, with 43% saying the economy worsened over the past 12 months.
On the policy front, weaker activity data and benign inflation support the start of a monetary easing cycle. The Selic rate stands at 15%, and a 50 basis points (bps) cut to 14.50% at the 17–18 March Copom meeting is expected. January IPCA inflation printed at 4.44% yoy, below the 4.50% upper the tolerance band for a third consecutive month. While services inflation and the tight labour market warrant caution, activity indicators point to accumulating restrictive effects, supporting a calibrated easing cycle.
Flávio Bolsonaro has advocated tax and spending cuts and a smaller state, but has yet to present detailed proposals or name an economic team. Market reaction will depend on whether concrete, orthodox fiscal measures emerge as the campaign progresses.
Chile: Gold production rose 27.1% in 2025 to 45,364kg, the highest level since 2014, while silver output increased 8.4% to 1,327,331kg, the strongest since 2015. The surge reflects favourable price dynamics and stronger by-product output from copper mining. Chile’s global ranking improved to 22nd in gold and 6th in silver production, reinforcing mining’s contribution to export revenues amid high metals prices.
Colombia: The presidential race remains highly competitive. An Atlas/Semana poll shows Abelardo de la Espriella at 28.4% and Iván Cepeda at 27.8% in the first round, with 7.7% undecided and blank or null votes exceeding any single trailing candidate. In a runoff, De la Espriella leads 36.8% to 34.6%, with 28% indicating blank or null votes. Senate voting intention shows the Historic Pact at 21.0% and the Democratic Center at 17.8%, suggesting a potentially more favourable congressional backdrop for a left-leaning administration. The congressional election takes place on the 8 March, ahead of the presidential election on the 31 May, and is likely to deliver a pivot towards the right, in our view.
Programmatically, De la Espriella advocates a pro-hydrocarbon pivot, state downsizing and a hard-line security agenda, while Cepeda represents continuity with Petro’s reform agenda, including energy transition and rural development. Fiscal clarity is limited on both sides, and markets will focus on post-legislative election alignment and potential finance minister appointments.
El Salvador: Moody’s affirmed the ‘B3’ rating and revised the outlook to positive, reflecting expectations of sustained fiscal consolidation under the International Monetary Fund (IMF) programme. The fiscal deficit is projected at 3.0% of GDP in 2025, narrowing to 2.3% in 2026 and 2.2% in 2027. GDP growth is forecast at 4.0% in 2025 and 3.1% in 2026. While liquidity buffers and fiscal credibility have improved, high debt and pension-related liabilities remain structural constraints.
Mexico: The central bank held the policy rate at 7.00% and reiterated a dovish bias, with Governor Victoria Rodríguez signalling that easing could resume once tax and tariff impacts prove transitory. Core inflation remains elevated at 4.5% yoy in January, and the bank now expects the 3.00% target to be reached only by Q2 2027. Market expectations see end-2026 inflation at 4.1%. While a hold is expected in March, easing could resume in Q2, though credibility risks remain if cuts exceed 50bps in 2026.
Central and Eastern Europe
Data suggests monetary policy unchanged for now.
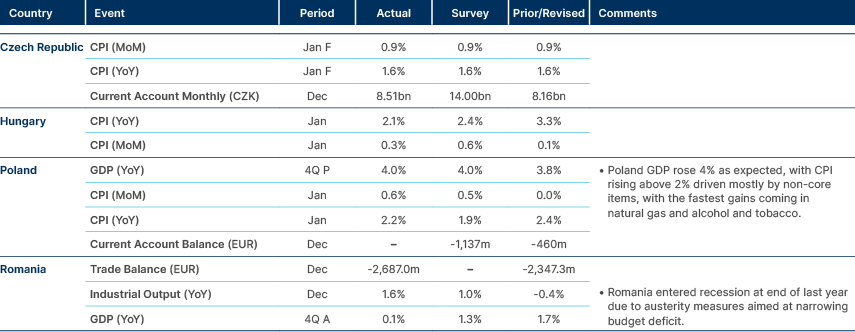
Romania: The external trade deficit narrowed 19.7% yoy to EUR 2.7bn in December, marking the eighth consecutive month of contraction. Exports rose 9.4% yoy, while imports declined 0.4% yoy. For 2025, exports increased 4.2%, led by autos (3.5% yoy; 46.6% share of total exports), edible oils, fuels and manufactured goods. The annualised trade deficit fell to 8.64% of GDP at end-2025 from 9.44% a year earlier, with the nominal gap at EUR 32.7bn. Softer domestic demand should continue to compress imports in coming months.
Türkiye: President Recep Erdoğan reshuffled the cabinet, appointing hardline Istanbul chief prosecutor Akın Gürlek as Justice Minister and Mustafa Ciftci as interior minister. Gürlek assumes Chairmanship of the Council of Judges and Prosecutors, consolidating influence over judicial appointments nationwide. The move signals intensifying legal pressure on opposition figures ahead of the 2028 elections. Markets will monitor potential institutional and governance implications.
Middle East and Africa
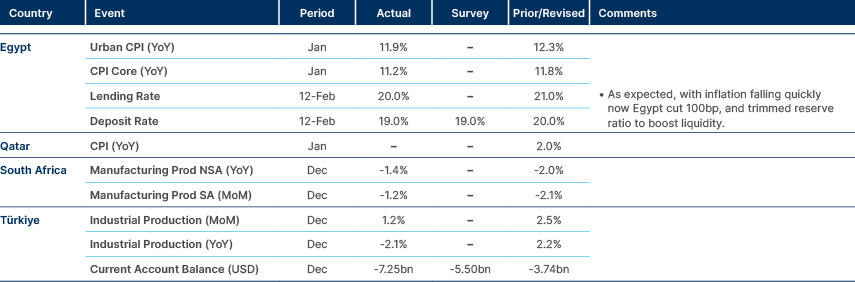
Egypt cut policy rates by 100bps and RRR by 200bps.
Angola: The first copper and cobalt shipment was delivered via the Lobito Atlantic Railway, reducing transport times from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) by roughly seven days. The corridor spans around 1,300km to the DRC border with a 450km extension to the Copper Belt and is backed by roughly USD 1bn in investment plus EUR 600m from EU-linked financing. It operates under a 30-year concession and is expected to generate USD 1.6–3.4bn annually over 30 years. The project enhances Angola’s strategic role in critical minerals supply chains.
Developed Markets
Mixed labour market data amidst softening inflation
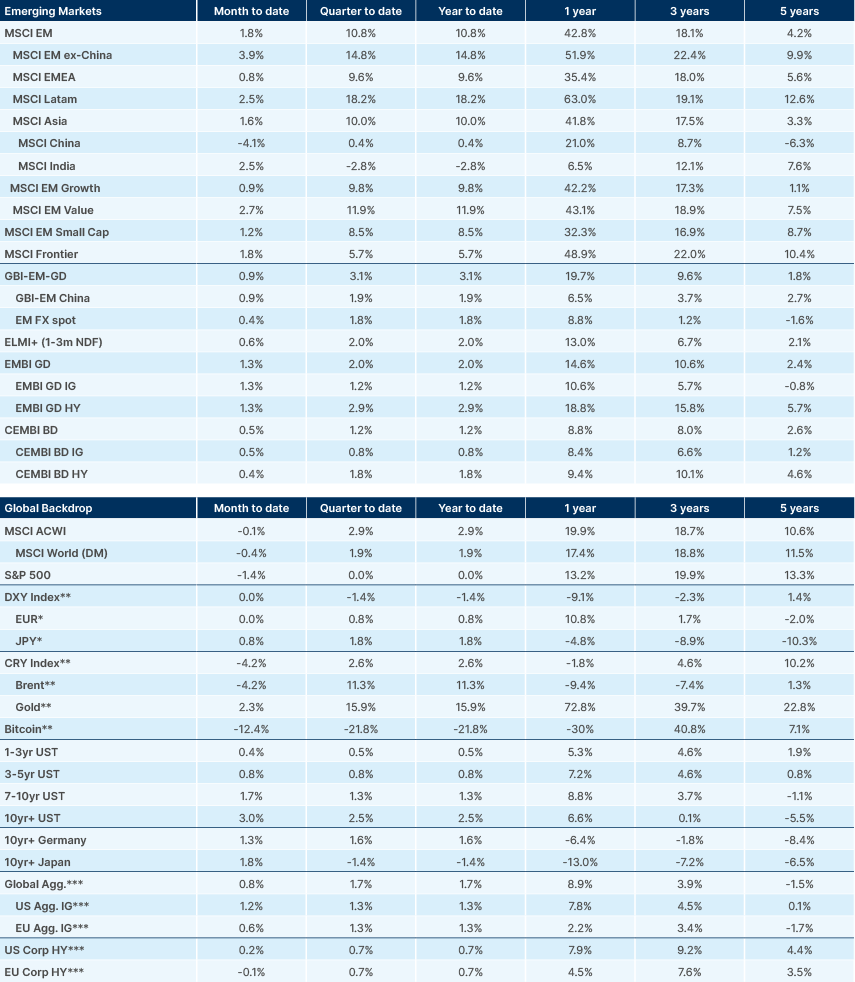
Benchmark Performance
Source and notations for all tables in this document:
Source: Bloomberg, JP Morgan, Barclays, Merrill Lynch, Chicago Board Options Exchange, Thomson Reuters, MSCI. Latest data available on publication date.
* Price only. Does not include carry. ** Global Indices from Bloomberg. Price to Earnings: 12m blended-forward
Index Definitions:
VIX Index = Chicago Board Options Exchange SPX Volatility Index. DXY Index = The Dollar Index. CRY Index = Thomson Reuters/CoreCommodity CRM Commodity Index.
Figures for more than one year are annualised other than in the case of currencies, commodities and the VIX, DXY and CRY which are shown as percentage change.