
- Strong jobs data last week led to higher US yields and put further pressure on global equities.
- Oil rose above USD 80.
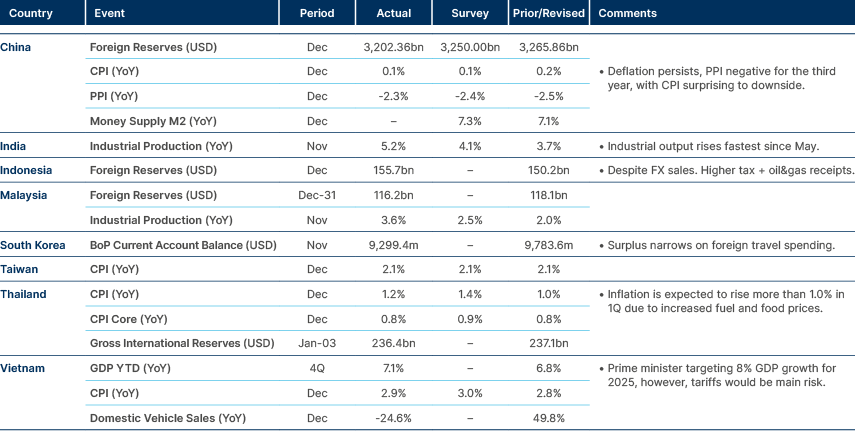
- China posted another record trade surplus in December.
- Moody’s upgraded Argentina’s foreign currency ceiling from Caa3 to Caa1.
- Fitch upgraded El Salvador’s credit rating from CCC+ to B-.
- In Croatia, President Milanovic was re-elected in a landslide victory.
- General Joseph Aoun wins the presidency in Lebanon after a second-round.
- Ecuador announces general election in February, Gabon’s presidential election expected in March.
- A tax amnesty programme in Morocco generated USD 12.7bn in declared assets.
Last week performance and comments
Global Macro
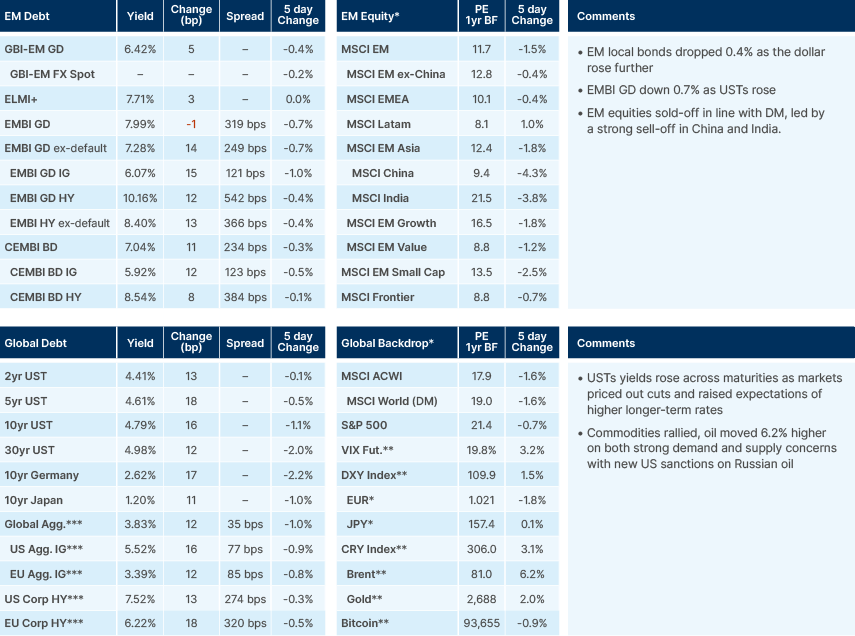
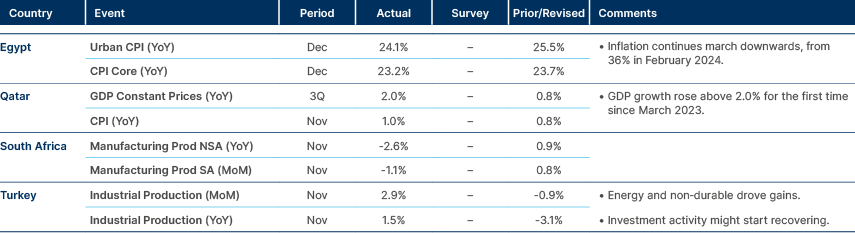
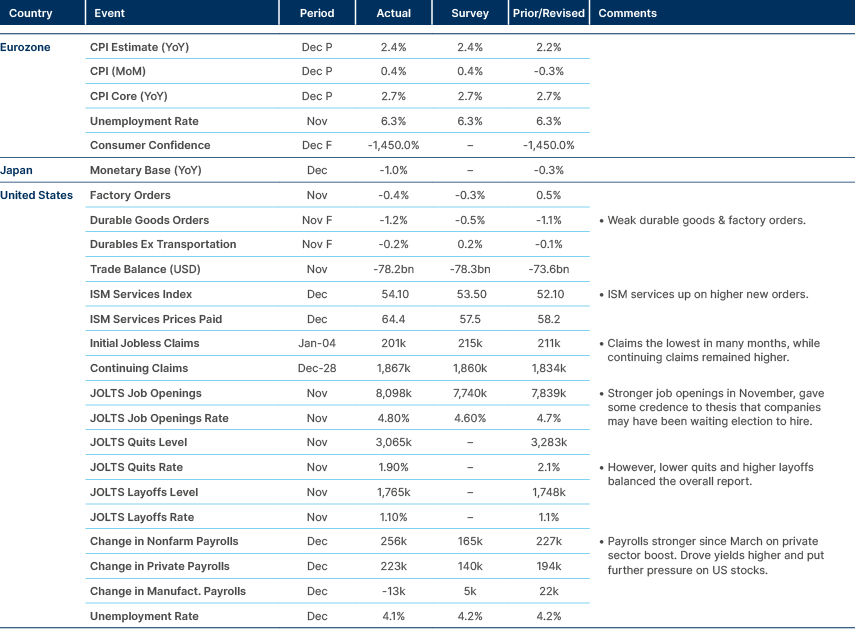
Strong US jobs data last week led to a rise in inflation expectations and another leg up in yields. Non-farm payrolls increased by 256k in December, beating the consensus estimate of 165k. The three-month moving average of payrolls is now at 170k, from 113k in August, and the six-month average rose to 165k from 142k, the first rise since May 2024. The unemployment rate also fell to 4.1%, a sign the US labour market is stabilising. The yield curve continued to steepen, driven also partially by expectations that US Treasury issuance under President Trump will be weighted more heavily toward the long end of the curve.
The market is now pricing only 25 basis points (bps) cut this year. Last week Bank of America joined the cohort of sell-side banks calling for no more cuts in 2025 which includes BNP Paribas and Deutsche Bank. The conversation could move to rate hikes if the core personal consumption expenditures (PCE) index moves above 3% and expectations de-anchor. The University of Michigan’s one-year inflation forecast surged from 2.8% to 3.3%, albeit the expectation was highly skewed by Democrat Party members who now sees inflation at 4.3% (from 1.5% in September) whilst republicans see inflation at 0.1% (from 3.6% in September).
While the strength of the US economy presumably makes markets more sensitive to an inflation upside surprise in this week’s consumer price index (CPI) release, the yield levels reached further out on the curve seem to have generated an uptick in natural demand for bonds. The bigger pressure points from a positioning standpoint seem to be US equities, where there is growing nervousness that we are on the cusp of higher yields triggering a larger wave of systematic selling.
The S&P500 rose by more than 20% in each of the past two years. This has happened just four times in the past 150 years, and on only one of those occasions did the index rise further in the third year, which was in the long bull market of the 1990s. However, yields were grinding lower in this period, and it appears that with bond yields and stocks now firmly inversely correlated since December, a further leg up for equities will be difficult if yields rise. A second wave of inflation and more issuance of long-term Treasuries presents the biggest risk to the US exceptionalism consensus.
Commodities
Oil prices rose to a three-month high, now trading above USD 81 per barrel. Strong Chinese demand, cold weather in the US and Europe, lower US inventories and strong US economic data were driving demand. On the supply side, the latest batch of US sanctions put pressure on Asian buyers of Russian crude. The reversal took place at the end of 2024 when oil positioning was extremely light.
Emerging Markets
Asia
No inflation in Asia. Indo FX reserves solid.
China
December’s trade surplus reached a record USD 104.8bn, exceeding the consensus estimate of USD 100bn, as both imports and exports outperformed expectations. The People’s Bank of China (PBoC) continued to tighten liquidity in the onshore market with the seven-day repo fixing rising 32bps as tax payments approach and the PBoC limits the size of its open market operations. Meanwhile, the USD/CNY fixing came in slightly lower at 7.1885 (-6 pips), signalling the central bank’s ongoing efforts to stabilise the currency. To address RMB weakness, the PBoC has announced measures to increase cross-border macro adjustment parameters, enabling more cross-border financing, and collaborated with the Hong Kong Monetary Authority to establish a RMB 100bn trade finance facility.
Chinese companies Tencent, an internet conglomerate, and Contemporary AMP (CATL), a global leader in the production of Ion batteries were added to the US Defence Department list as a ‘Chinese Military Company’. Both companies have publicly refuted the claims and highlighted they are neither military companies nor suppliers. Both are seeking to appeal the decision and to be removed from the list. There have been cases of successful repeals in the past. The US Defence Department list is not related to OFAC's Special Designated Nationals (SDN) List. This is managed by the Treasury's Office of Foreign Assets Control and often triggers sanctions and prohibitions.
Indonesia
Bank Indonesia continues to “guard the currency’s stability” through interventions in the spot, domestic non-deliverable forward and bond markets. The central bank’s Director for Monetary and Asset Securities Management, Edi Susianto, told Bloomberg “we are in the markets to ensure the balance of foreign exchange supply and demand to maintain market confidence.”
Latin America
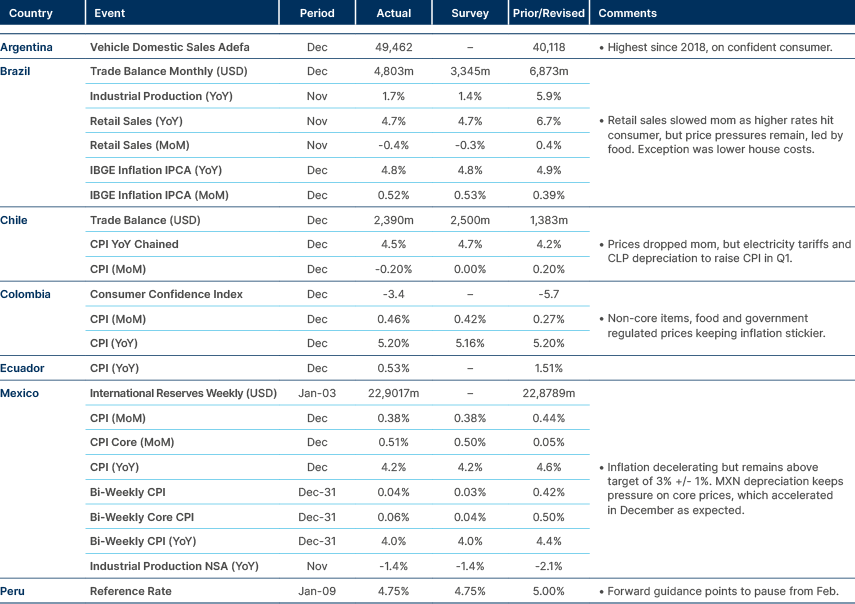
CPI inflation remains sticky in Brazil and Colombia, converging to target in Mexico.
Argentina
Moody’s raised Argentina’s local currency ceiling from Caa1 to B3 and its foreign currency ceiling from Caa3 to Caa1. This allows corporates to be upgraded several notches above the sovereign, which is rated Ca by Moody’s. The upgrade reflects greater predictability and consistency in economic policy, which has led to a rapid reduction in monetary and fiscal imbalances. Moody’s said the Argentinian government has eased restrictions on cross-border payments and foreign exchange (FX) convertibility, increasing foreign currency liquidity. There has also been a shift toward reducing the role of the state in the economy, with fewer interventionist policies that lower the risk of transfer and convertibility issues in the event of a sovereign debt default.
Ecuador
A presidential election will be held on 9 February. To win in the first round, a candidate needs at least 40% of the vote and a 10% margin over the second candidate. According to limited polls, the incumbent President Daniel Noboa is likely to win a second term in office, most likely after a second-round vote on 13 April.
El Salvador
Fitch upgraded El Salvador’s long and short-term credit ratings from CCC+ to B- with a stable outlook. The upgrade reflects lower financing needs and easing of financing constraints after regaining market access and more International Monetary Fund (IMF) support. The new IMF programme is expected to support fiscal consolidation and the reduction of outstanding short-term debt owed to domestic banks.
Central and Eastern Europe
Croatia
President Zoran Milanović was re-elected in a landslide victory with 74.7% of the vote against HDZ candidate Primorac who won 25.3%, broadly in line with exit polls. Milanovic has been one of Croatia's most polarising political figures. While the presidency is largely ceremonial, Milanovic is known for his outspoken leadership style and controversial statements. This represents a strong blow to the HDZ (The Croatian Democratic Union) and the government, a proof that people are dissatisfied with them.
Central Asia, Middle East, and Africa
Africa’s reformists making further progress.
Gabon
Reuters initially reported that Gabon's transition leader, General Brice Oligui Nguema, announced elections for 22 March, only to retract the report an hour later. However, Jeune Afrique suggests the 22 March date may still be officially confirmed in the coming days. A Q1 presidential election is anticipated, given the success of the constitutional referendum last month. This election should mark the end of the transition period of military rule since the previous president was ousted in August 2023.
Nguema has also revealed that Gabon has sought technical assistance from the IMF to assess its financial situation, potentially paving the way for a broader economic programme. Nguema’s buy-in for an IMF programme is seen as pivotal, as he is widely expected to secure the presidency. The combination of a successful election and a robust economic framework could signal a turning point for Gabon, laying the groundwork for stability and growth in the post-transition era.
Ghana
President John Mahama has scrapped seven government ministries to 23 as part of a cost-saving measure under the IMF’s austerity programme.
Lebanon
General Joseph Aoun, the chief of the Lebanese Armed Forces (LAF), was elected president in two rounds, securing an absolute majority of votes. This was the first time the consensus candidate has won the presidency in Lebanon since the country’s civil war ended in 1990. Aoun is seen as a pro-west/Saudi candidate, which will help with the reconstruction of the state, although is considered as less hardline on the Hezbollah faction than some. The next step will be to elect a Prime Minister. Lebanese bonds have risen rapidly in recent weeks, but the timeline towards an IMF programme and eventual restructuring remains lengthy, and the state of Lebanon’s finances is difficult to discern after years of Hezbollah rule.
Morocco
A tax amnesty programme has generated USD 12.7bn in declared assets, with direct revenue of USD 600m for the state treasury in 2024. This programme targeted individuals who had not declared taxable profits and income in Morocco before January 2024.
Developed Markets
Stronger US service sector and job markets surveys.
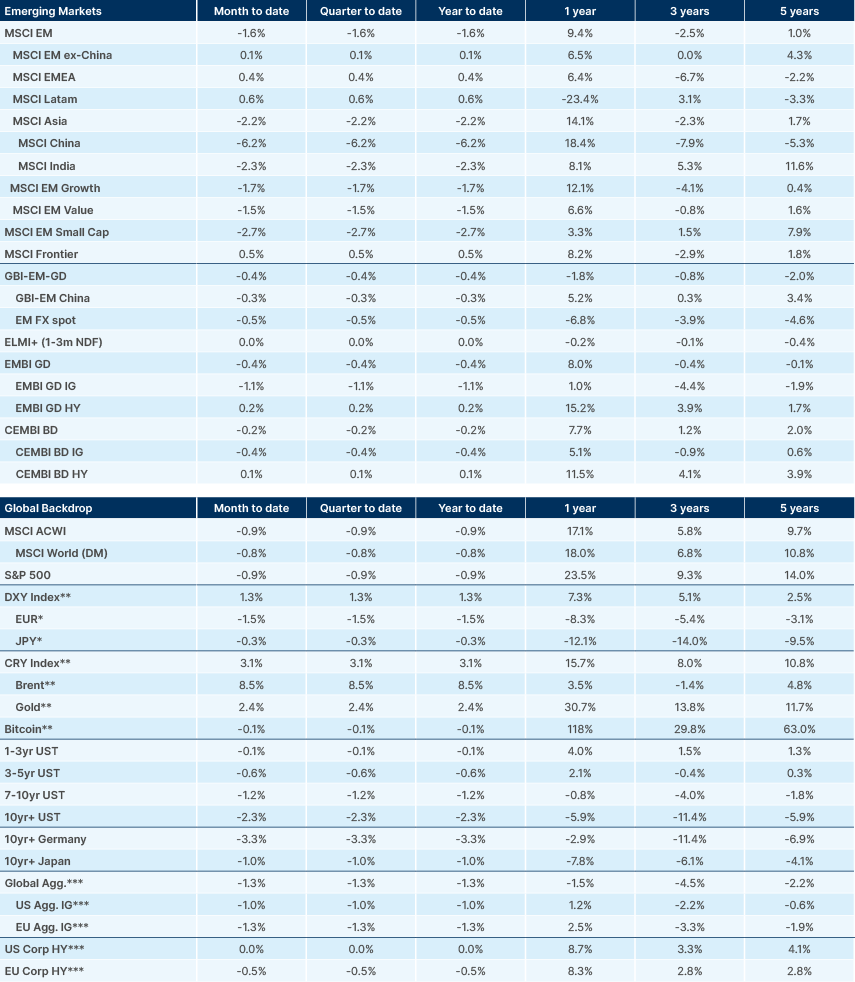
Benchmark performance
Source and notations for all tables in this document:
Source: Bloomberg, JP Morgan, Barclays, Merrill Lynch, Chicago Board Options Exchange, Thomson Reuters, MSCI. Latest data available on publication date.
* Price only. Does not include carry. ** Global Indices from Bloomberg. Price to Earnings: 12m blended-forward
Index Definitions:
VIX Index = Chicago Board Options Exchange SPX Volatility Index. DXY Index = The Dollar Index. CRY Index = Thomson Reuters/CoreCommodity CRM Commodity Index.
Figures for more than one year are annualised other than in the case of currencies, commodities and the VIX, DXY and CRY which are shown as percentage change.