
- US and China established a preliminary framework on trade.
- Bessent identified five leading candidates for Fed Chair.
- China’s Fifth Plenum underscored technology and innovation as primary strategic objectives.
- US announced sanctions on Russian refineries, targeting facilities supplying Asian markets.
- Chinese industrial profits rebounded sharply in September, rising 22% yoy.
- Bank Indonesia should gradually cut policy rates to around 3.5%, according to Finance Minister.
- South Korea and US trade negotiations stalled ahead of the upcoming APEC summit.
- Argentina’s ruling La Libertad Avanza Party secured a decisive midterm election victory.
- Moody’s estimated the US effective tariff rate on Mexico at 7.5%, 6% below initial forecast.
- Bahrain and Saudi Arabia signed a new industrial trade pact under the Takamul initiative.
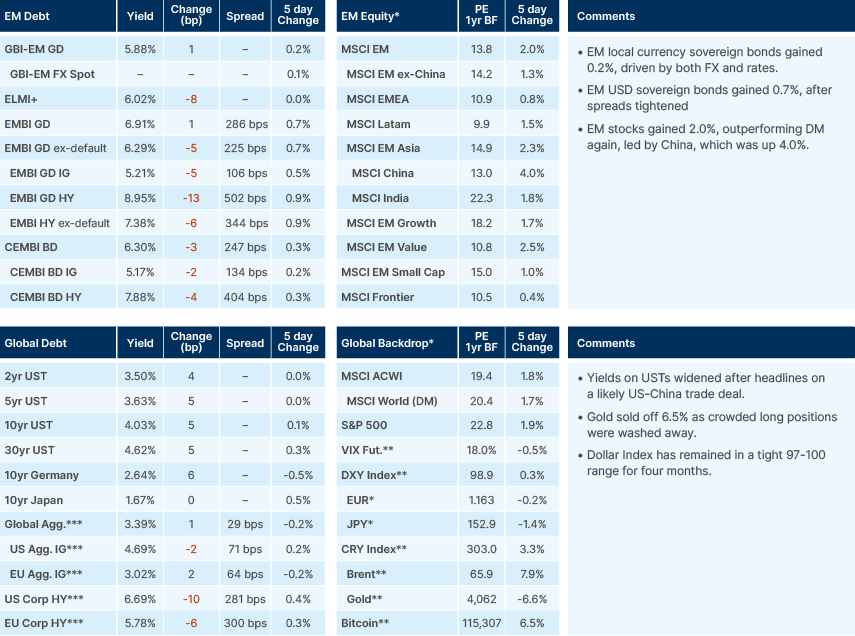
Last week performance and comments
Global Macro
US and Chinese trade negotiators convened in Malaysia ahead of the scheduled meeting between presidents Donald Trump and Xi Jinping on 30 October. According to recent media reports, both sides have established a preliminary framework, with growing optimism that a comprehensive trade agreement could be finalised by Thursday. US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent noted that the discussions encompass agricultural purchases and the sale of rare earth materials. Meanwhile, the Chinese Communist Party’s official publication urged the world’s major economies to “jointly safeguard the hard-won achievements” stemming from the latest round of trade negotiations.
In other news, Bessent identified the five leading candidates for the position of the next Chair of the Federal Reserve (Fed): current Fed Board members Christopher Waller and Michelle Bowman; former Fed Governor Kevin Warsh; White House National Economic Council Director Kevin Hassett; and BlackRock Inc. executive Rick Rieder. None of those is surprising. We are likely to see a list with two finalists by Thanksgiving and the announcement by January.
On monetary debasement, recent data from Bank of America Merrill Lynch shows that gold inflows over the past four months have exceeded the cumulative total of the preceding 14 years. Nonetheless, the premise of widespread currency debasement is inconsistent with current market and fiscal indicators: the 10-year US Treasury yield dipped below 4% last week, and the federal government recorded a budget surplus in September.
Another global highlight last week was China’s Fifth Plenum, which underscored technology and innovation as primary strategic objectives for the next five years. The agenda prioritised tech self-reliance, stronger domestic demand, and an expanded global presence, aimed at addressing subdued internal consumption and an increasingly adverse external environment. The emphasis on disruptive innovation and the development of core technologies highlights Beijing’s determination to resolve supply-chain bottlenecks through home-grown capabilities, with supply-oriented policy reforms expected to materialise in 2026, focusing on infrastructure and technological advancement.
The Plenum’s social welfare agenda suggests a more gradualist policy approach than some hoped. Efforts to manage economic rebalancing and alleviate social pressures such as “anti-involution” are likely to remain modest in the short term. The commitment to building a “unified national market” was mentioned briefly in connection with enhancing social mobility, employment, and income distribution. This implies to us that reflation is unlikely to be a key policy priority in 2026, even as the leadership reaffirmed its intention to stimulate consumption and effective investment.
Finally, the Plenum introduced a new long-term target for 2035: to “greatly enhance global impact.” This objective extends beyond economic measures, signalling China’s ambition to strengthen its international standing through soft power and the promotion of cultural innovation.
On US corporate earnings, 138 companies within the S&P 500, representing approximately 25% of the index’s market capitalisation, have reported Q3 results to date. Of these, 78% have exceeded earnings per share expectations, 79% have surpassed sales forecasts, and 66% have outperformed on both metrics. However, early indications suggest that tariffs are beginning to weigh on certain segments of the US equity market. Tesla reported a 40% yoy decline in operating profit – its fourth consecutive quarter of disappointing results – largely attributable to margin compression from elevated input costs and intensifying price competition in the electric vehicle market. Operating expenses rose 50% yoy to USD 3.4bn, with tariff-related costs alone exceeding USD 400m.
Commodities
The US announced additional sanctions on Russian refining operations, targeting key facilities that supply Asian markets. As a result, shipments of Russian crude and refined products to major Indian refiners are projected to decline sharply, potentially to near zero, according to industry executives. The move triggered a nearly 4% intraday spike in Brent crude prices, with the futures curve shifting back into backwardation.
The sanctions have disrupted established arbitrage flows and are expected to exert greater pressure on refined product prices than on crude directly. India currently imports approximately 1.6-1.7 million barrels per day (mbpd) of Russian crude, including 0.6–0.7mbpd by state-owned refiners, making it one of Russia’s largest buyers since the onset of the war in Ukraine. China, which imports around 2mbpd of Russian crude, may also face secondary effects if enforcement measures are expanded.
The issue is anticipated to feature in discussions between President Trump and President Xi, introducing additional uncertainty around the scope and implementation of secondary sanctions. While Brent crude prices have rebounded from the USD 60 per barrel level, events earlier this year suggest that geopolitical market rallies tend to fade, leaving the underlying market tone broadly bearish to 2026.
Gold and silver experienced their steepest single session declines in over a decade, with spot gold falling more than 5% and silver nearly 10%. The sharp correction appears to mark the exhaustion phase of the recent gold rally, reflecting a position reset following several months of sustained inflows.
Emerging Markets
Asia
China’s GDP remains strong, driven largely by exports.
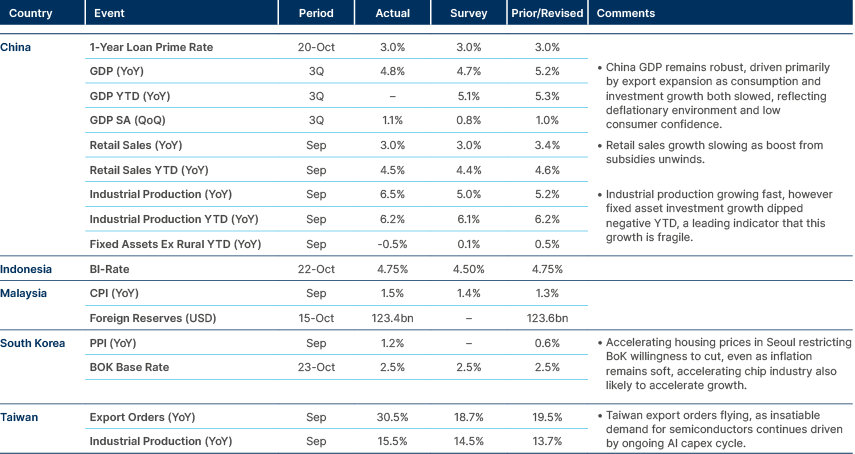
China: Industrial profits recorded a sharp rebound in September, rising 21.6% yoy – the steepest since November 2023 – and extending gains from 20.4% a month ago, according to data from the National Bureau of Statistics. While high-tech manufacturing earnings surged 26.8% last month, major industrial firms reported profits accelerating to 3.2% in September, up from 0.9% in January, amid official efforts to ease price wars.
India: The government announced plans to overhaul its key economic indicators in 2026, including revisions to GDP, CPI, and industrial output statistics. The update will introduce a new services sector index and rebase GDP calculations to 2022–2023 prices. The objective of the revamp is to more accurately capture the growing contribution of digital and services-led activity to the economy and to enhance the overall reliability and transparency of official data.
Indonesia: Finance Minister Purbaya Sadewa indicated that Bank Indonesia should begin a gradual easing cycle, targeting a policy rate of around 3.5%, roughly 1% above the current inflation rate. The central bank has already implemented 75 basis points (bps) of rate cuts this year but has maintained policy settings approximately 2% above CPI inflation to preserve currency and financial stability.
South Korea: Trade negotiations between South Korea and the US remain stalled on several key issues ahead of the upcoming APEC summit. Media reports indicate Seoul is considering a phased investment plan, allocating approximately USD 25bn annually over eight years, rather than committing the full USD 350bn upfront. In other news, North Korea conducted a short-range missile test – its first in five months – just days before the summit, adding a layer of regional uncertainty.
Meanwhile, the Bank of Korea kept its policy rate unchanged at 2.5% on a 5-1 vote, maintaining a dovish bias amid a rebound in semiconductor exports and renewed strength in property prices. The government extended existing fuel tax reductions for an additional two months and signalled potential reforms to lower the top dividend tax rate to 25%.
Pakistan: Islamabad announced a reduction in electricity tariffs for industrial and agricultural consumers of up to 40%, lowering rates to PKR 23 per kilowatt-hour to stimulate demand and enhance competitiveness. Separately, Pakistan and Afghanistan reached a ceasefire agreement brokered by Qatar and Türkiye, following recent border clashes that had heightened regional tensions.
Latin America
Brazil’s inflation falls below 5%.
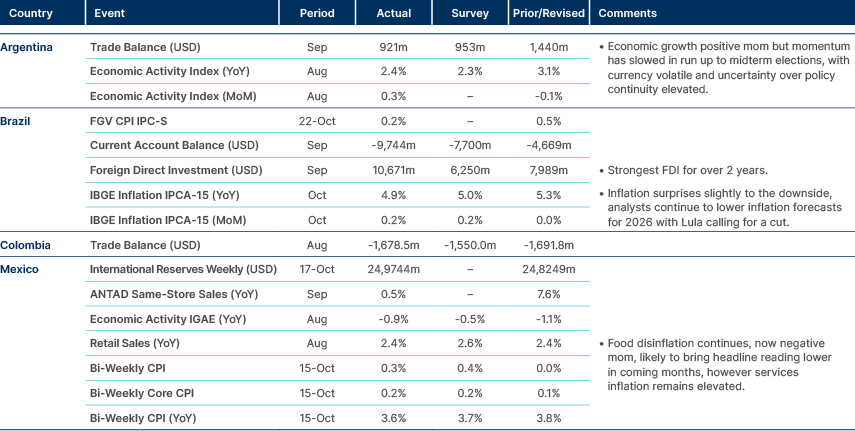
Argentina: Argentina’s ruling coalition, La Libertad Avanza (LLA), led by President Javier Milei, secured a decisive victory in the midterm elections. The party won 16 of 29 provinces and captured over 40% of the national vote, significantly ahead of the Fuerza Patria (Peronist) bloc. In the Province of Buenos Aires, despite earlier setbacks, including a 14-point margin for Kirchnerism in the regional midterms, the LLA-PRO alliance achieved a narrow win.
The victory is estimated to boost LLA seats in the Lower House to over 1/3 of the total, securing the minimum necessary to block any impeachment attempt even without support from its allies. The result, to us, is likely to cause further divisions within Peronism, which is already split in at least three groups (Cristina Kirchner; Axel Kicilloff; regional Peronists). Alejandro Catterbert from Poliarquía put it well: “Peronism is at its weakest point in terms of institutional power in a long time”
Turnout was very low at 67.9%, vs 72.2% in 2021 and 77.6% in 2017. Nearly 12 million voters stayed away from the polls, suggesting much of the “protest vote” that weakened Milei’s performance in the Province of Buenos Aires took the form of abstention rather than support for the opposition.
LLA’s strong showing gives Milei fresh political legitimacy and the legislative strength to pursue deeper reforms, particularly in tax and labour policy. Milei struck a conciliatory tone, highlighting the importance of consolidating the reforms over the next two years, and urging governors with parliamentary representation to engage in substantive dialogue and forge national agreements.
The victory also solidifies US backing which, alongside further reforms, including tax and labour markets, will allow the regime to dismantle capital controls, and accelerate the convergence to a floating FX regime. This would unlock further foreign direct investments, allowing for the accumulation of FX reserves and macro stabilisation ahead of the 2027 presidential election cycle.
In parallel, consumer confidence rebounded 2.5 points to 42.3 in October, recovering from September’s low. The government enacted, but subsequently suspended, unfunded education and healthcare spending measures pending the identification of financing sources by Congress.
Brazil: President Lula renewed pressure on the Central Bank of Brazil (BCB) to lower the benchmark Selic rate from its current level of 15%, aligning with his broader strategy ahead of the early 2026 re-election campaign. Fiscal challenges persist following the expiration of the IOF tax measure, which has reduced revenues by an estimated BRL 17bn. To offset the shortfall and maintain fiscal targets, the Finance Ministry is reportedly considering freezing up to BRL 7bn in congressional amendments.
Colombia: The August trade deficit was steady at USD 1.7bn, with imports up 7% yoy and exports down 0.1%. Manufacturing and consumer goods drove the imbalance, offsetting 13 months of falling fuel exports. China’s share of imports rose to 29%, surpassing the US at 20%, underscoring a shift in trade alignment.
Mexico: Moody’s estimated the US effective tariff rate on Mexico at 7.5%, nearly 6%below initial forecasts, as 85% of exports still qualify under USMCA rules. Mexico remains relatively insulated from US tariff actions, though the 2026 USMCA review poses renewed risk.
Peru: The Fiscal Council warned that Congress has approved 101 high-cost laws costing PEN 36bn a year (roughly 3% of GDP). It estimates the 2026 fiscal deficit could reach 5.5% of GDP if implemented, citing a weakened budget process and deteriorating fiscal discipline.
Central and Eastern Europe
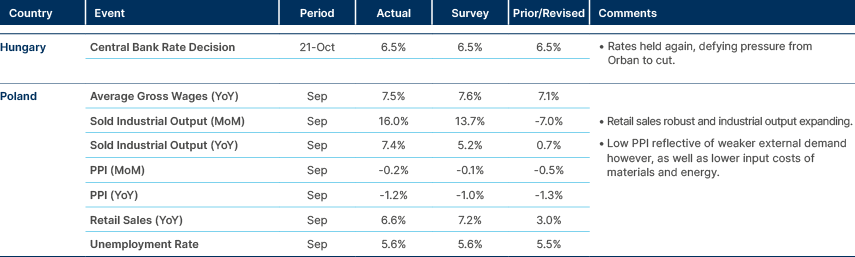
Hungary continue to hold rates, despite political pressure
Central Asia, Middle East, and Africa
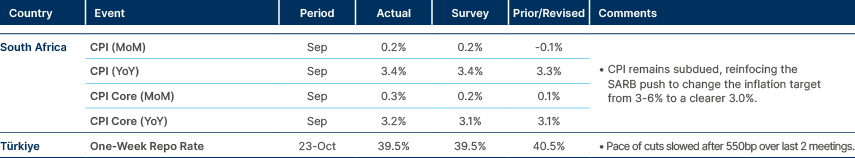
Türkiye cut rates again, but slowed the pace.
Across MENA, Fitch Ratings noted that sustained economic reform momentum and fiscal resilience are underpinning sovereign credit profiles, despite softer oil prices and elevated regional tensions. Most oil-exporting economies remain in fiscal surplus at crude prices around USD 70 per barrel, with the exceptions of Bahrain and Saudi Arabia. Meanwhile, non-oil economies such as Morocco and Egypt continue to benefit from robust domestic demand and rising investment inflows.
Türkiye: Parliament’s budget commission approved an omnibus fiscal bill targeting a TRY 350bn annual adjustment, including TRY 200bn in extra revenue and TRY 150bn in spending cuts. Measures include raising employer social security contributions, tightening rent tax exemptions, and reducing pension incentives. President Recep Erdoğan retains wide discretion over subsidy levels, with every 10% change in the private pension top-up altering costs by TRY 45bn. The 2026 budget debate begins this week.
Bahrain: Bahrain and Saudi Arabia signed a new industrial trade pact under the Takamul initiative to streamline customs and reduce export costs, strengthening bilateral industrial integration and investment flows.
Egypt: The General Petroleum Corporation will boost fuel imports by 60% yoy in November to free natural gas for export. The government cleared USD 9bn in arrears to foreign operators and authorised Shell and Petronas to ship 10 liquified natural gas (LNG) cargoes between November 2025 and March 2026. The move aims to stabilise FX reserves and attract new upstream investment.
Kazakhstan: The National Bank of Kazakhstan (NBK) said inflation pressures are being driven by excess liquidity from rapid credit growth and fiscal stimulus. Governor Timur Suleimenov urged tighter fiscal consolidation and pledged to withdraw liquidity via higher reserve requirements, expected to drain KZT 3.5trn from banks. The NBK may also limit domestic gold purchases to reduce money creation.
Morocco: The 2026 Finance Bill, approved by King Mohammed VI, focuses on social justice, territorial balance, and structural reform. The government allocated MAD 140bn to health and education (adding 27k jobs) and will advance public enterprise reform and governance modernisation. Real GDP is forecast at 4.8% in 2025, with inflation near 1.0%.
Nigeria: The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) is expected to cut the policy rate by 100bps to 26% in November after six months of disinflation, with September CPI inflation at 18%, the lowest in three years. Governor Olayemi Cardoso cited stronger FX reserves (USD 42.3bn) and exchange rate stability as grounds for easing. The CBN’s Monetary Policy Committee will also coordinate with the Finance Ministry to manage excess liquidity from fiscal inflows.
Qatar: Following the EU’s planned 2027 ban on Russian LNG, both Qatar and the US are set to expand export capacity substantially. The US is targeting an additional 50 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) of LNG output, while Qatar’s North Field expansion will lift production to 126mtpa by 2026. Together, these increases are expected to offset much of the lost Russian supply, with limited impact on European gas prices given the diversified sourcing and stable demand outlook.
Tunisia: The government plans a TND 1.4bn (EUR 400m) Eurobond or private placement in 2026 – its first market issue since 2019 – as part of efforts to diversify funding sources. Domestic borrowing remains dominant, with the central bank providing TND 11bn in liquidity support (41% of financing needs). Fitch recently upgraded Tunisia to ‘B-’ with a stable outlook.
Developed Markets
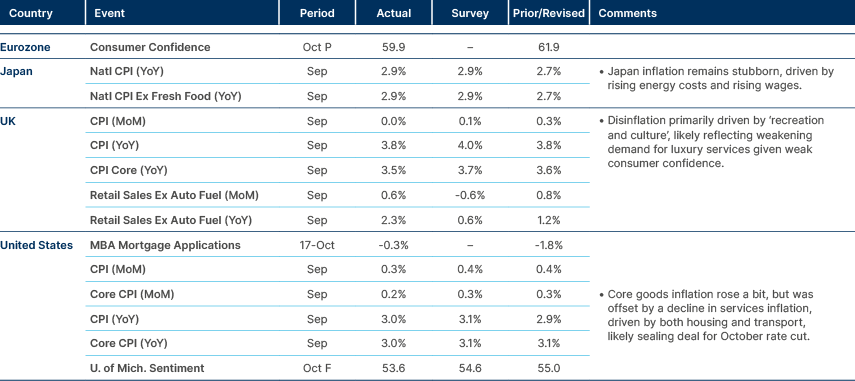
Inflation data surprised to the downside in US and UK.
Japan: Despite having been in her position for less than a week, Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi’s government is already winning plaudits, with the Nikkei newspaper poll showing approval ratings touching 74%. Broadcaster ANN put her popularity at 58.7%, while newspapers Asahi and Mainichi reported 68% and 65% rates, respectively.
Benchmark Performance
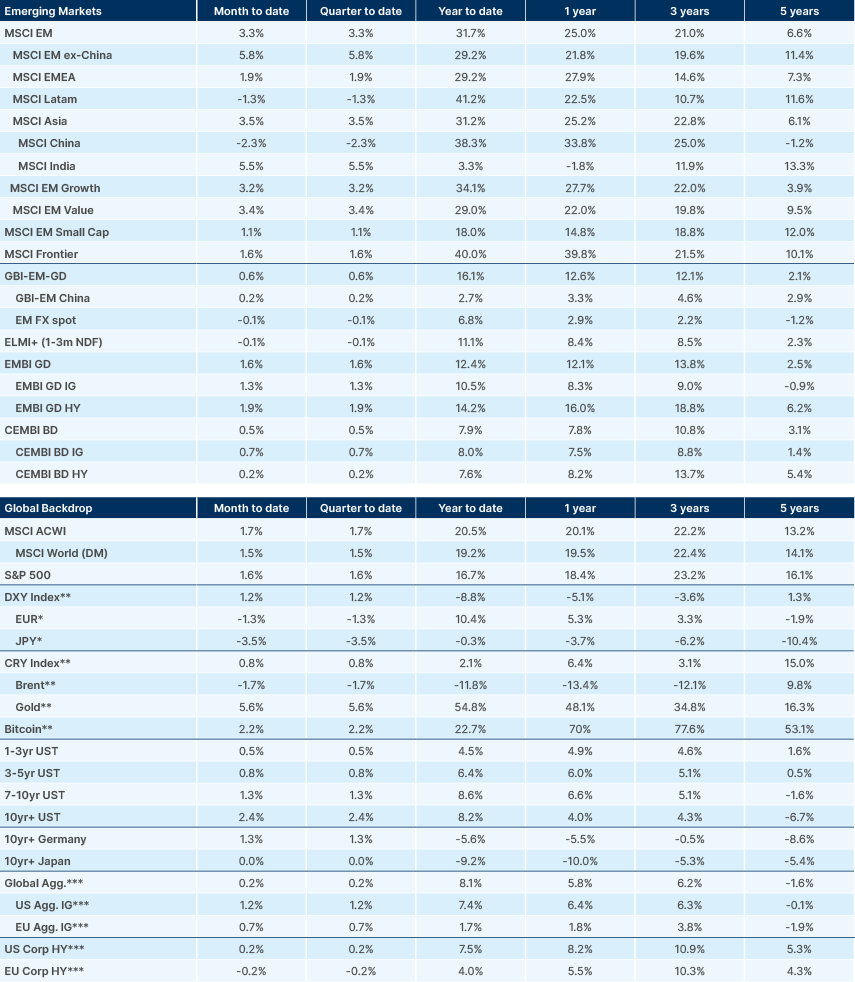
Source and notations for all tables in this document:
Source: Bloomberg, JP Morgan, Barclays, Merrill Lynch, Chicago Board Options Exchange, Thomson Reuters, MSCI. Latest data available on publication date.
* Price only. Does not include carry. ** Global Indices from Bloomberg. Price to Earnings: 12m blended-forward
Index Definitions:
VIX Index = Chicago Board Options Exchange SPX Volatility Index. DXY Index = The Dollar Index. CRY Index = Thomson Reuters/CoreCommodity CRM Commodity Index.
Figures for more than one year are annualised other than in the case of currencies, commodities and the VIX, DXY and CRY which are shown as percentage change.